Architects: Want to have your project featured? Showcase your work through Architizer and sign up for our inspirational newsletters.
Mexican architecture is as varied and inspiring as the country itself. From expansive deserts to lush rain forests and towering mountains, local landscapes have shaped architects’ varied approaches to building across Mexico’s temperate to tropical zones. In these climates, a range of open-air architecture is being built that reimagines how to connect people with their surroundings. From small pavilions to large complexes, these structures take inspiration from the places they are built for.
Taking a deeper dive into Mexican architecture through drawings, the following open-air projects are found nationwide. Images of each completed project are juxtaposed with plan drawings to show how the buildings are organized to encourage movement between spaces. While the projects are programmatically and spatially diverse, they each explore views and Mexican culture and how to design for local climates. Made for the changing conditions and shifting light throughout the day, these projects and drawings embody what it means to build in Mexico today.
Telcel Theater
By Ensamble Studio, Mexico City, Mexico
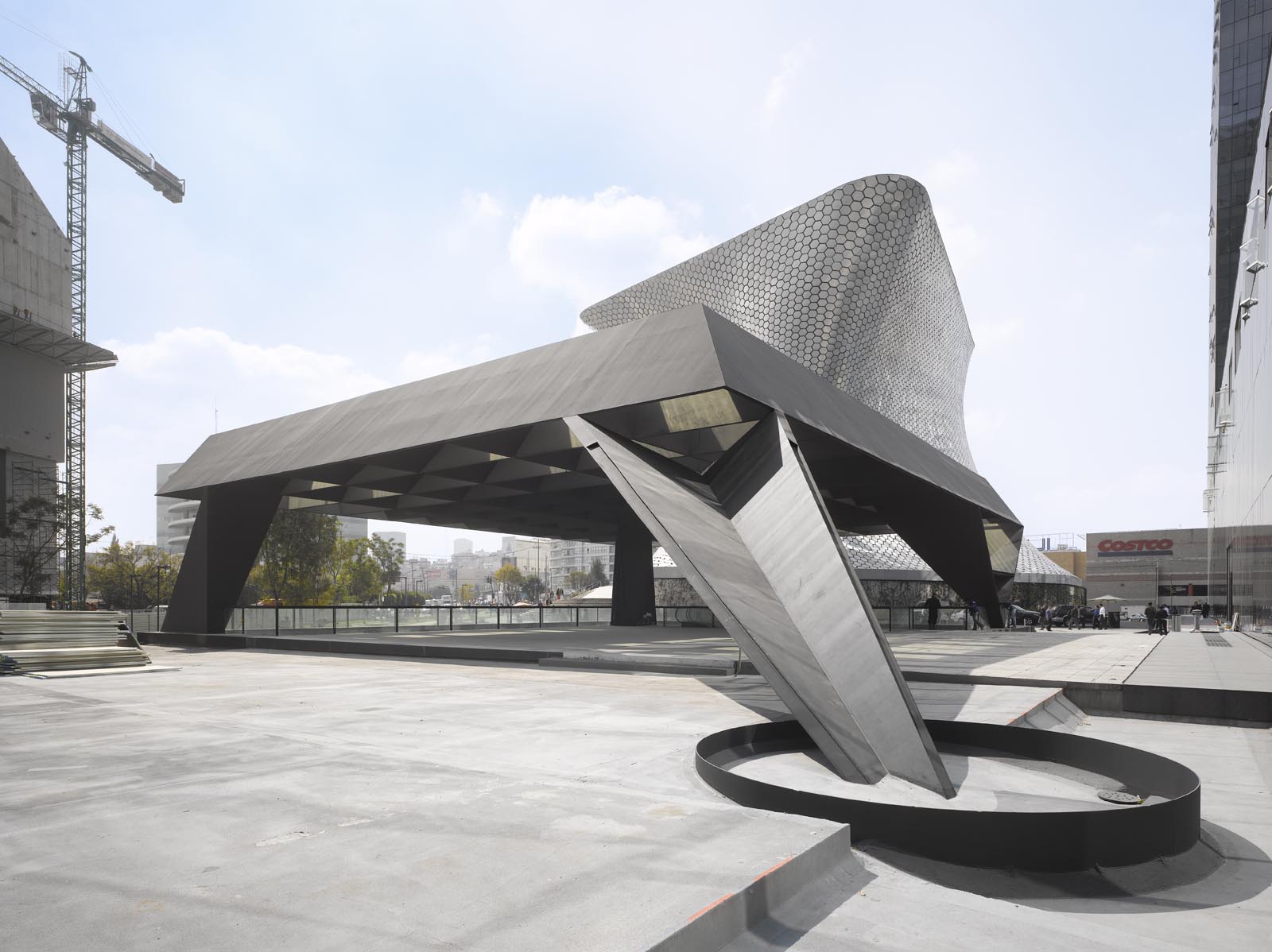
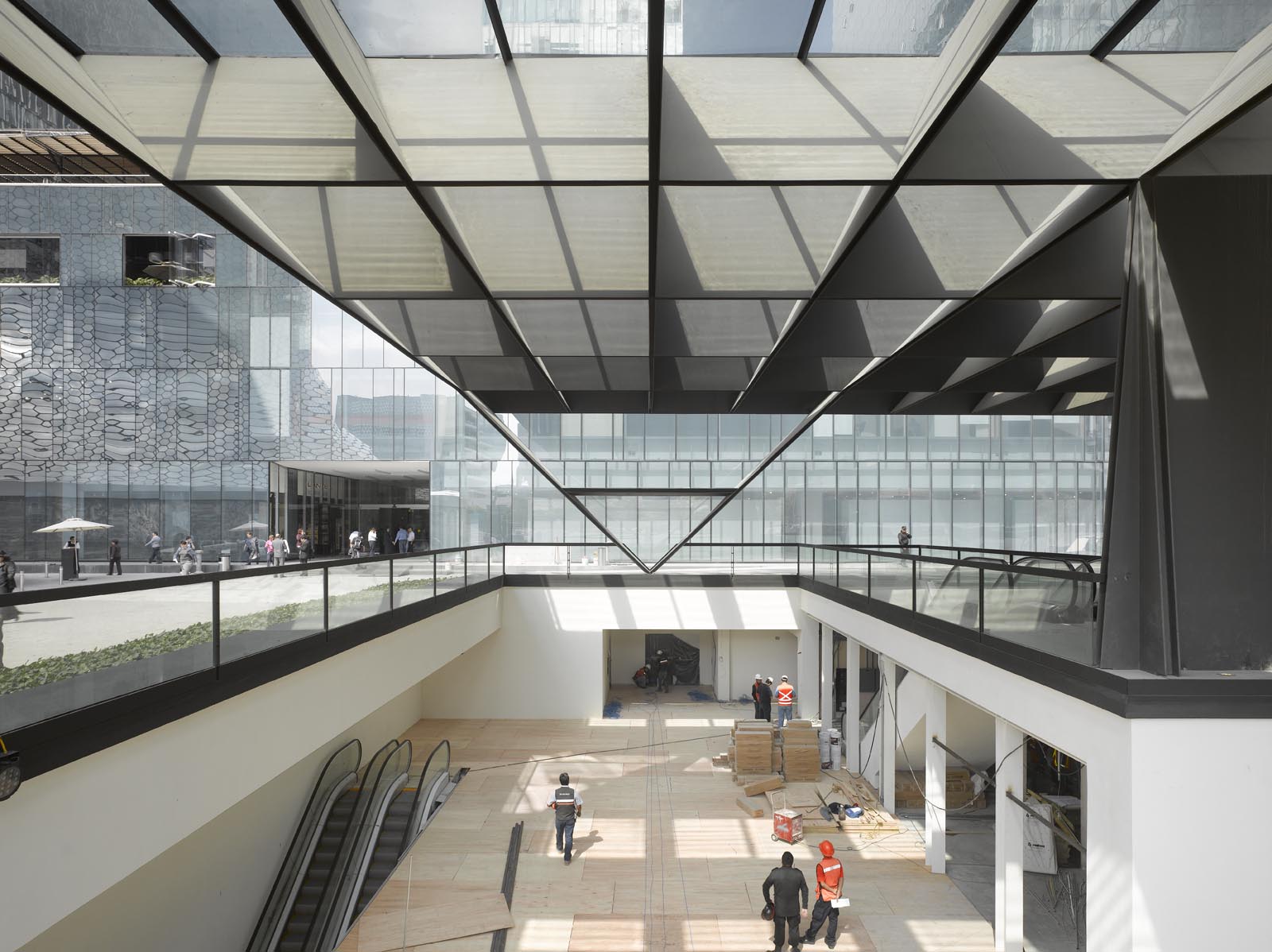


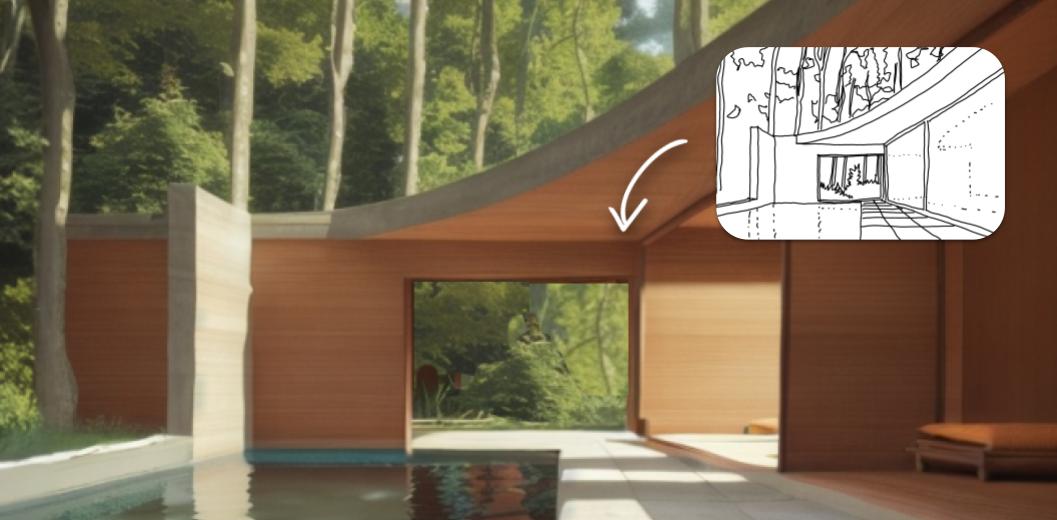
 Ensamble’s design for the Telcel Theater was buried underground with a large metallic structure lifted from ground level. This creates a dramatic open-air volume that rises above and below the ground. The structure above appears as a stone of air, supported by the space that comes from a sequence of excavated terraces. Below, the excavated spaces are given to the public and open to the sky, protected by the symbolic metal structure.
Ensamble’s design for the Telcel Theater was buried underground with a large metallic structure lifted from ground level. This creates a dramatic open-air volume that rises above and below the ground. The structure above appears as a stone of air, supported by the space that comes from a sequence of excavated terraces. Below, the excavated spaces are given to the public and open to the sky, protected by the symbolic metal structure.
As the design team notes, the project confronts the elemental natures with which it is built: the deep density of the negative space, of vertical character; and the horizontal tension of the air contained and supported by the Dovela metal structure. The plan drawing shows the outline of this canopy as it rises above the open excavated lobbies below. Once inside the earth, the Theater appears as the end of a sequence of spaces.
Community Center San Bernabé
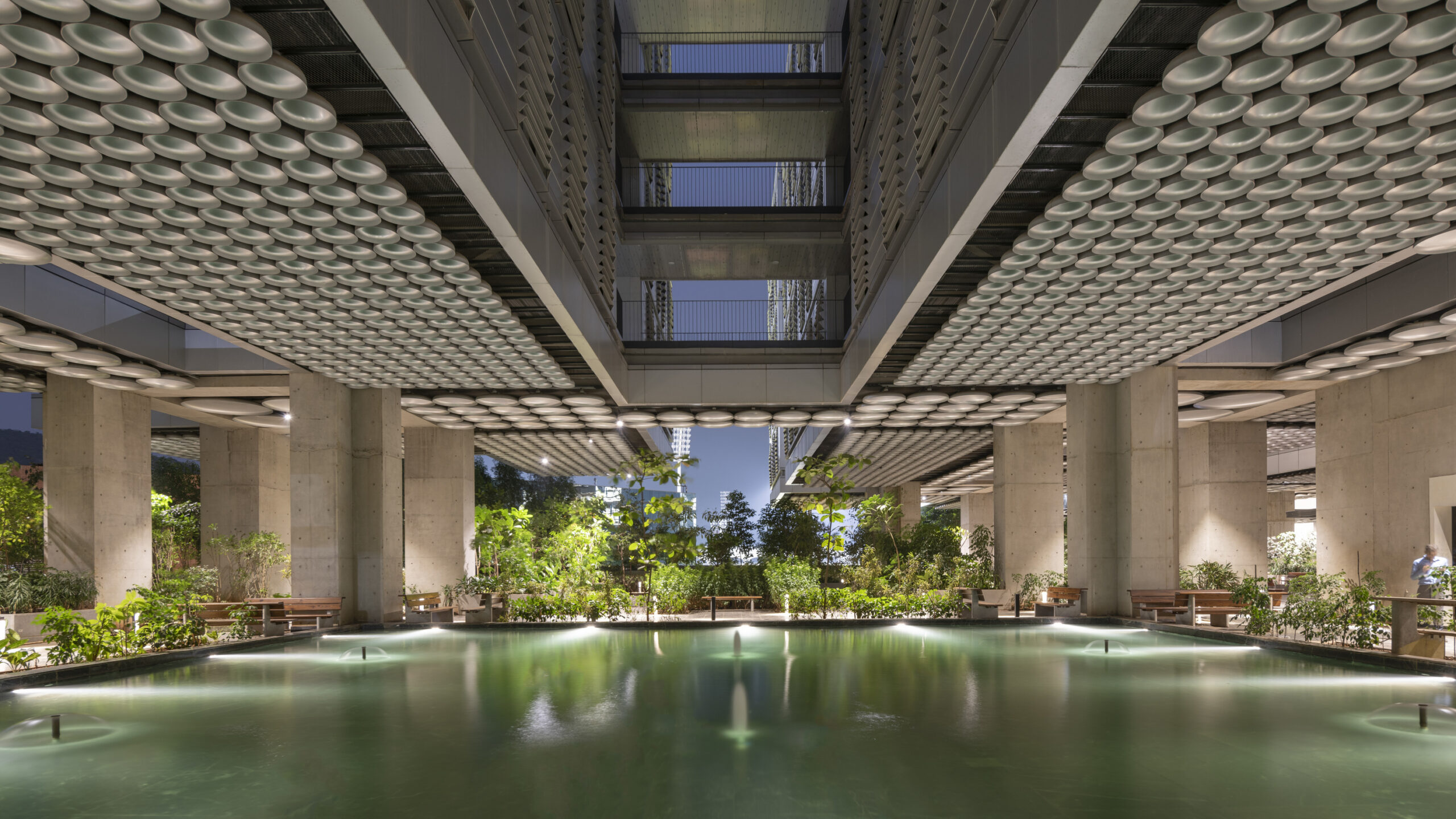
By Picharchitects/Pich-Aguilera, Monterrey, Mexico
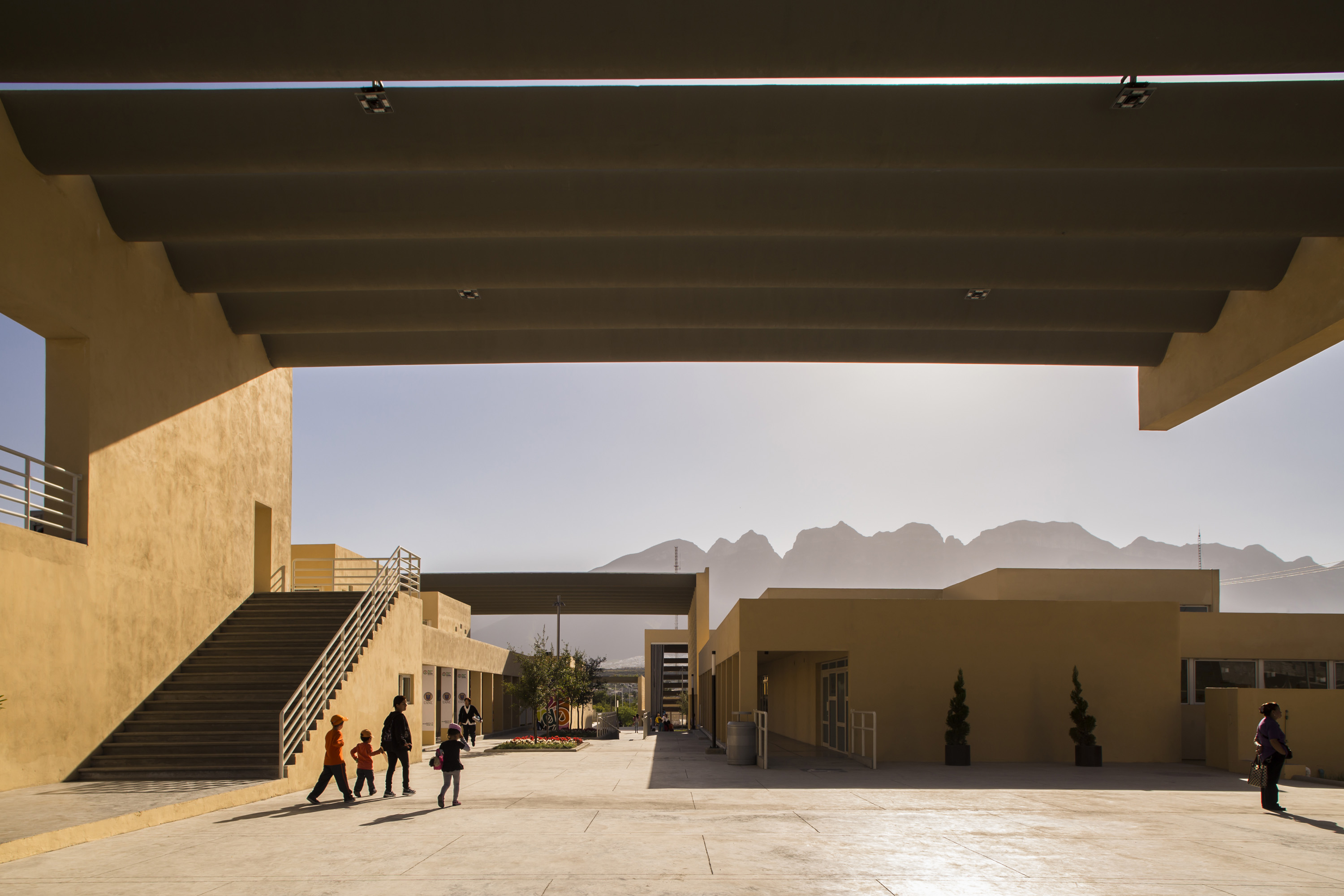
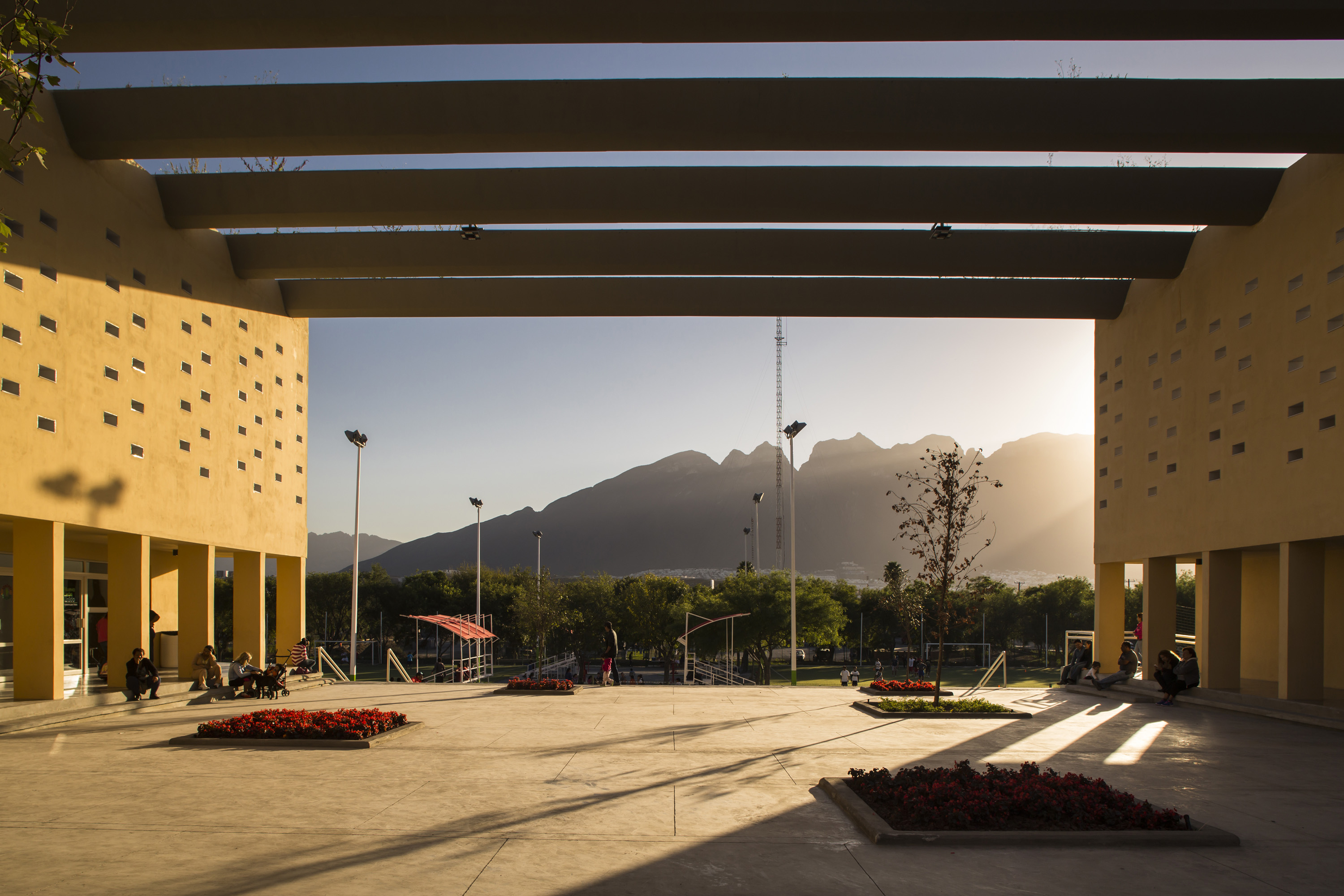


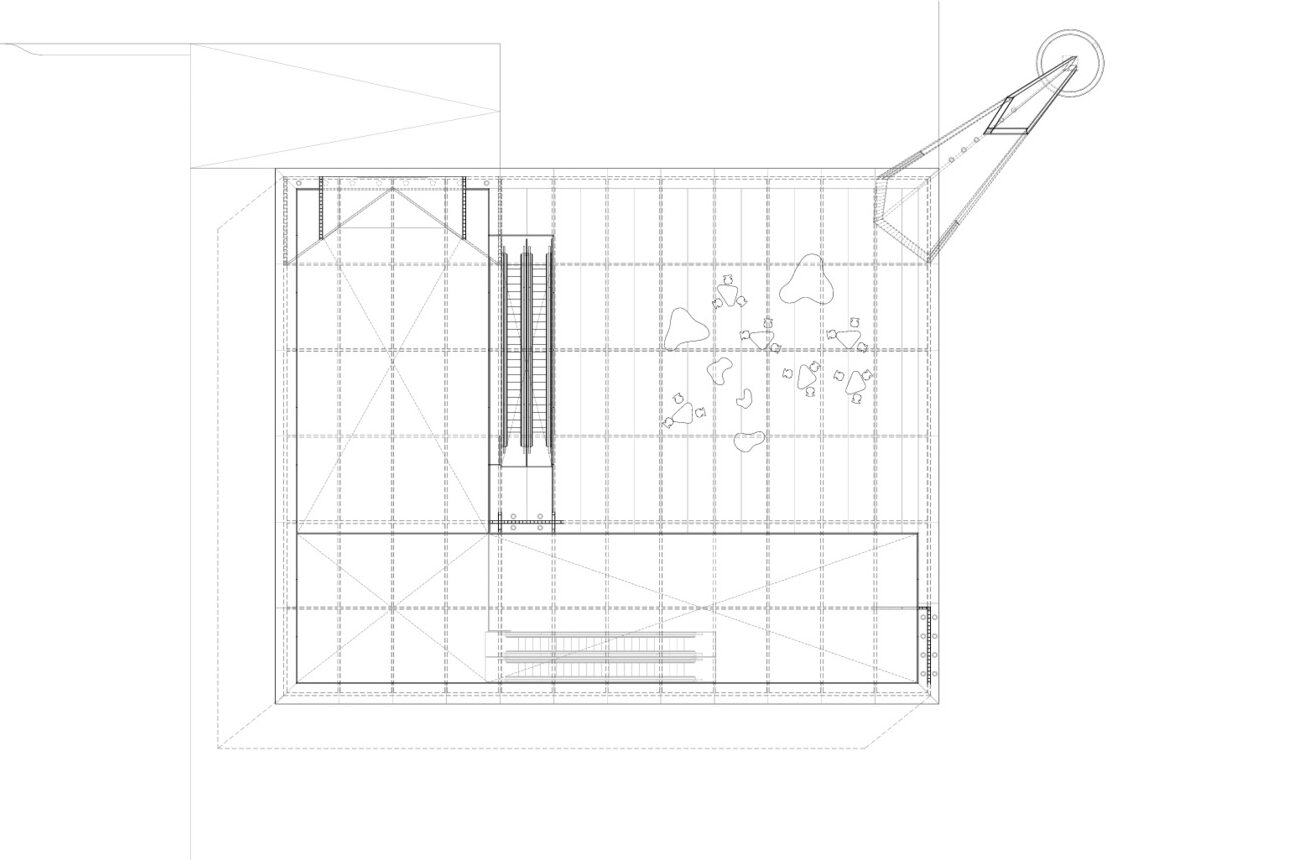
 Designed for the community center of San Bernabé, this project offers a building-street which aimed to transmit civic values inherent to the urban structure of the neighborhood. This building-street was conceived as a framework for the relationship and the expression of individuals and the community, so that it will be getting stronger as the citizens start to discover it and living freely in it.
Designed for the community center of San Bernabé, this project offers a building-street which aimed to transmit civic values inherent to the urban structure of the neighborhood. This building-street was conceived as a framework for the relationship and the expression of individuals and the community, so that it will be getting stronger as the citizens start to discover it and living freely in it.
As seen in the open-air plan drawing, this street built within acts like the backbone of the built bodies that house the functional program of the community center and responds to an urban vision as a whole. The project also includes an allocation for renewable energy production, integrated into the architecture from the system of “solar beams” that make up the shade structure.
Mar Adentro
By Taller Aragonés / Miguel Ángel Aragonés, San José del Cabo, Mexico
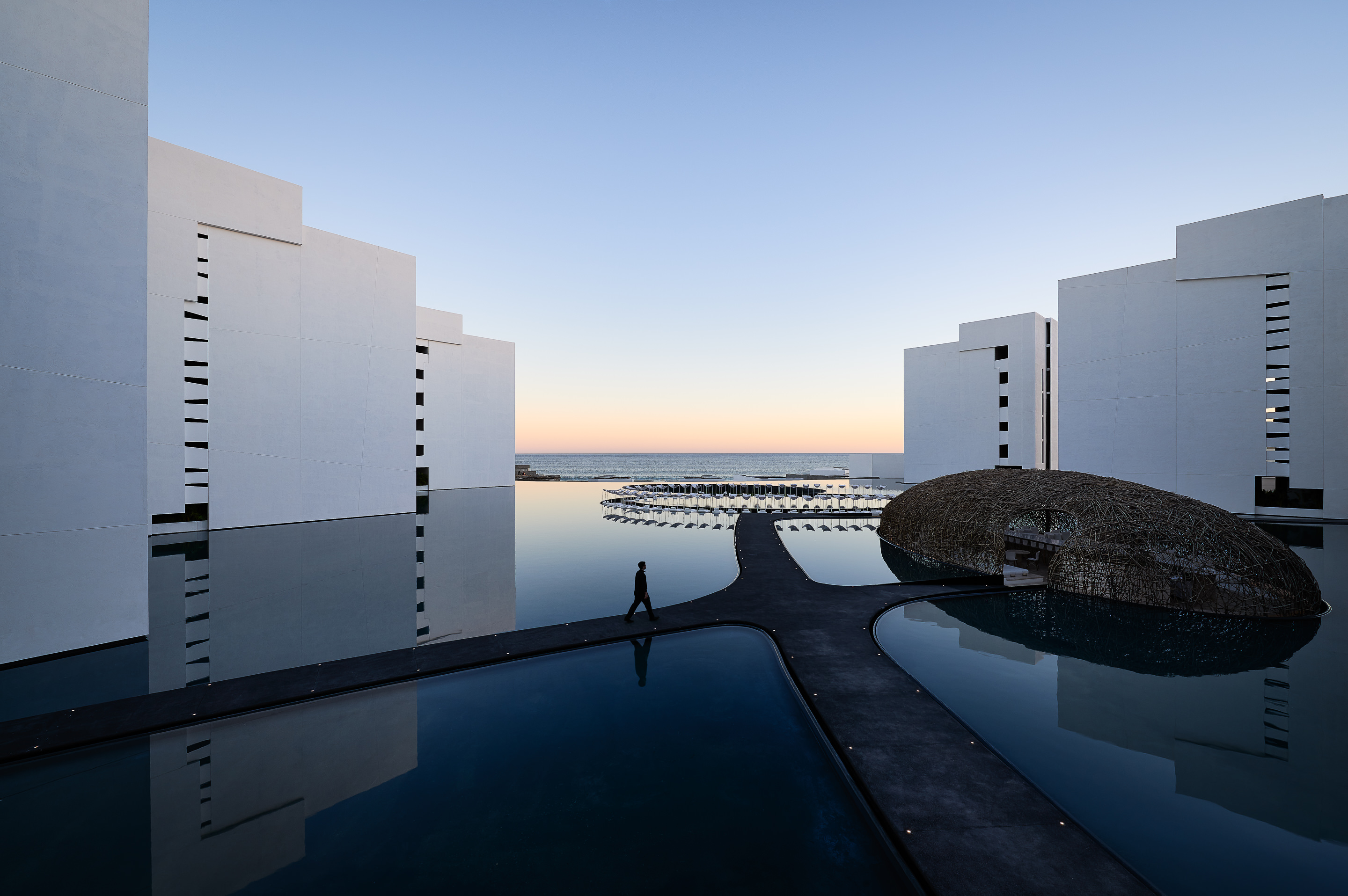
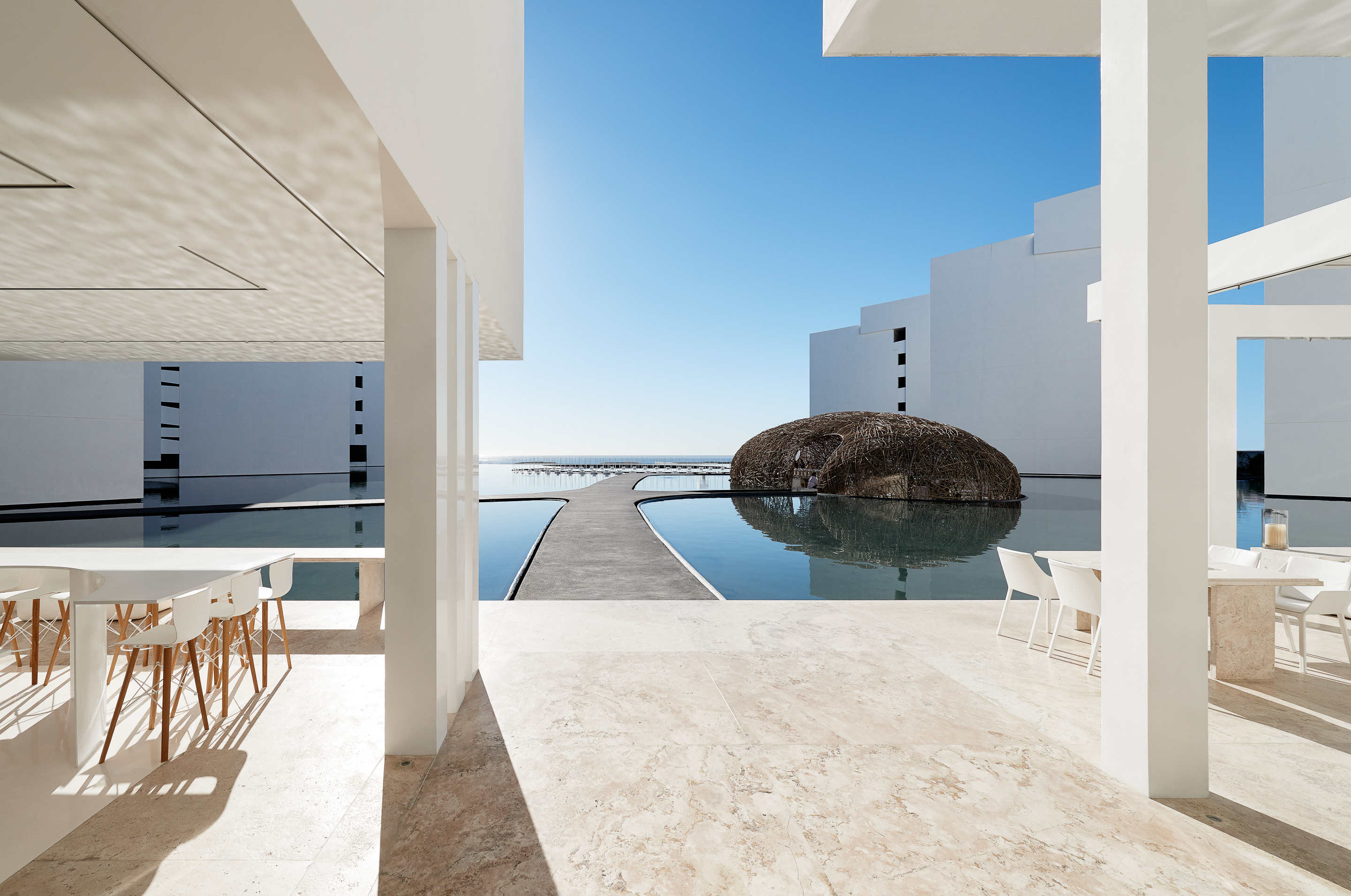


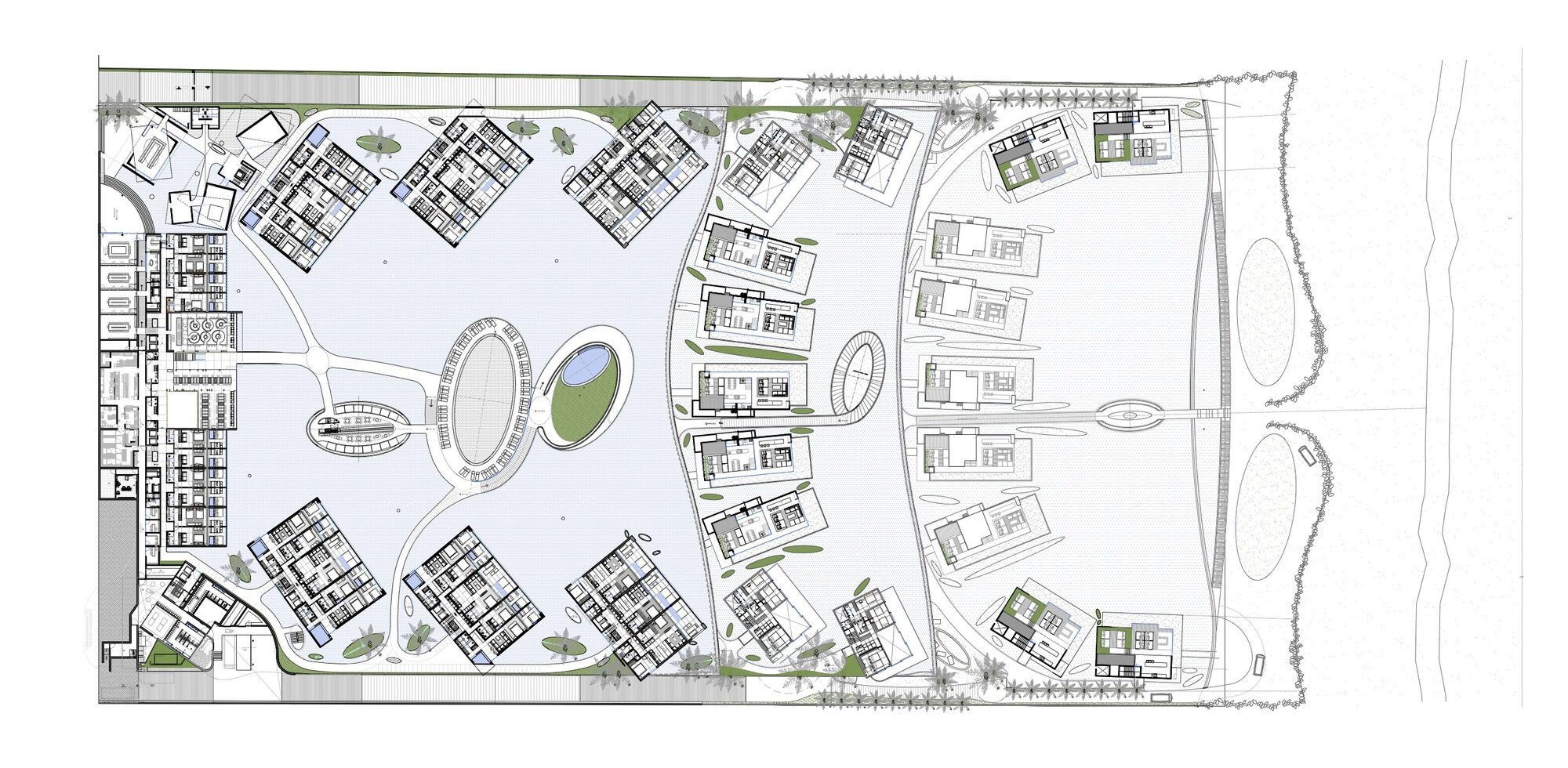 Mar Adentro was inspired by the “enormous drive of water under a scorching sun.” This piece of land, located in the middle of a coastline dotted with “All Inclusives,” and the team wanted to challenge what would have been a box similar to other structures in place. The central idea was to take the horizon and bring it into the foreground. Mar Adentro is a kind of Medina that opens out onto the sea.
Mar Adentro was inspired by the “enormous drive of water under a scorching sun.” This piece of land, located in the middle of a coastline dotted with “All Inclusives,” and the team wanted to challenge what would have been a box similar to other structures in place. The central idea was to take the horizon and bring it into the foreground. Mar Adentro is a kind of Medina that opens out onto the sea.
Describing the project, the team notes that, “the water is an event that borders the entire project; all of the volumes open up toward the sea and turn their backs on the city.” Each floating volume contains interiors that form, in turn, independent spaces. All rooms were prefabricated for construction ahead of time in a factory. The important thing is the versatility of this structure, one that can be entirely factory-made then raised on site in a straightforward manner.
Ecumenical Chapel
By Bunker Arquitectura, Cuernavaca, Mexico
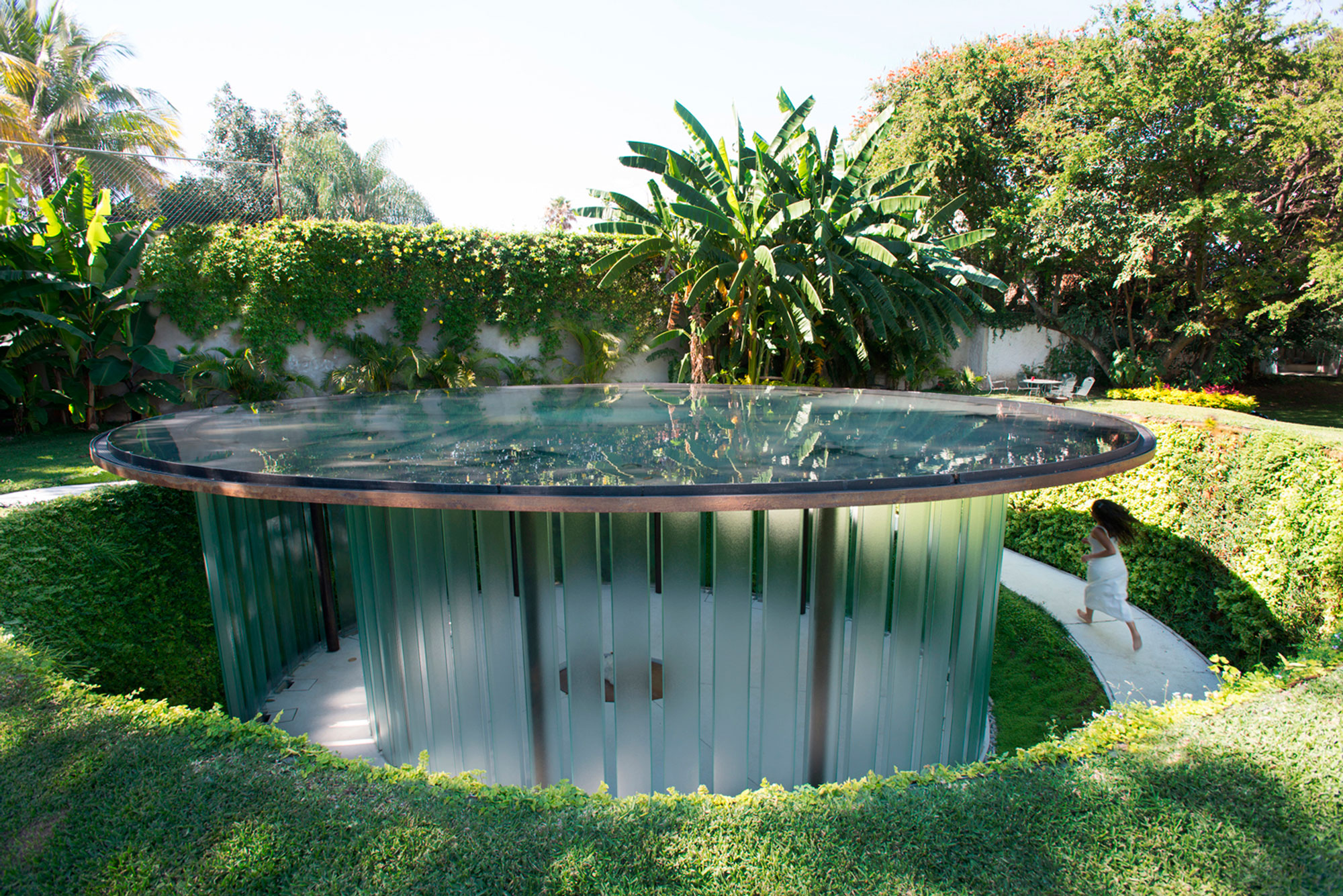
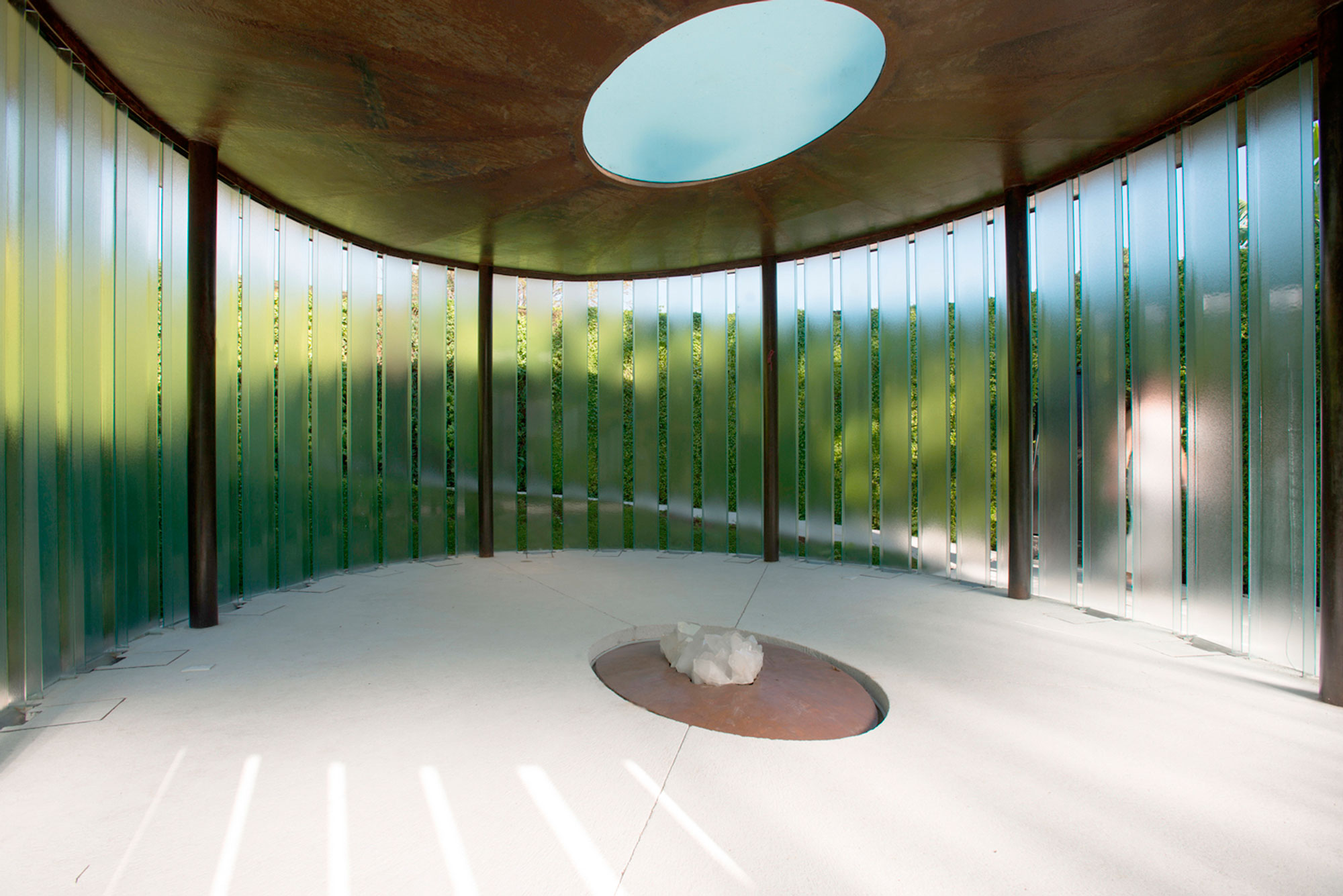


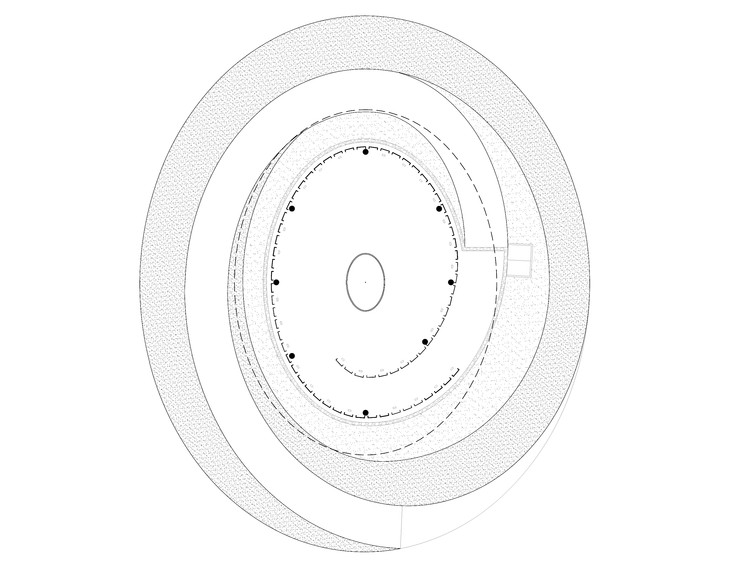
This private chapel was made for a plot of land recently bought on the backside of a weekend house in Cuernavaca, Mexico. The clients wanted an Ecumenical chapel, a non-religious and universal space, to meditate. The chapel is buried underground and a spiraling ramp that surrounds it brings visitors inside. This ramp is flanked with a vegetated wall that functions as a vertical garden.
Outside, a water pond forms the rooftop of the chapel. At its center there is an oculus, a glass covered opening in the metallic plate, that lets sunlight filter through the water, generating light and shadow patterns on the inside. The space is contained by a lattice wall formed by separated glass beams that lets the air flow through its inside. The oculus and simple support structure that connects to the landscape is seen in plan.
Centinela Chapel
By Estudio ALA, Arandas, Mexico


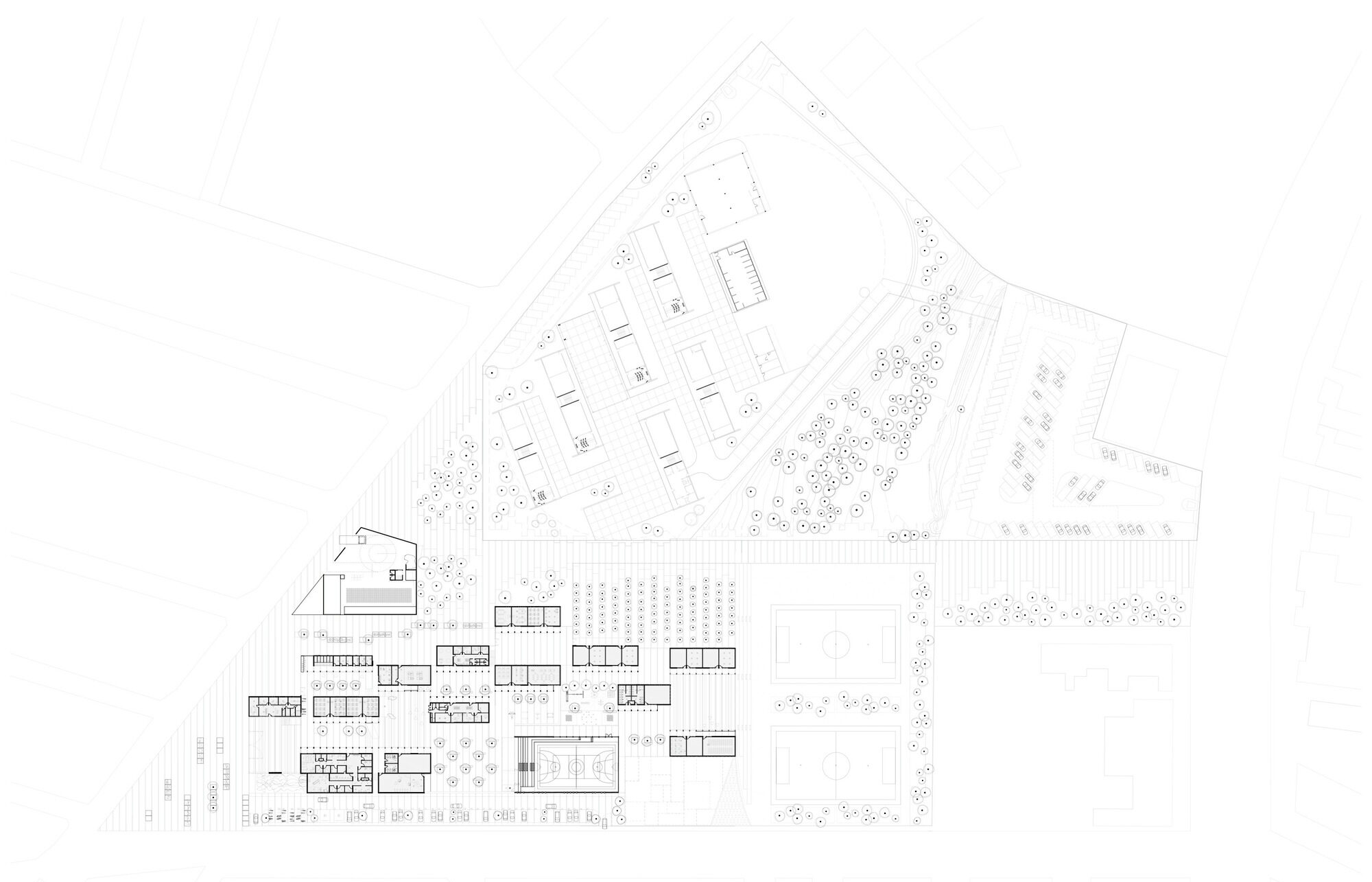
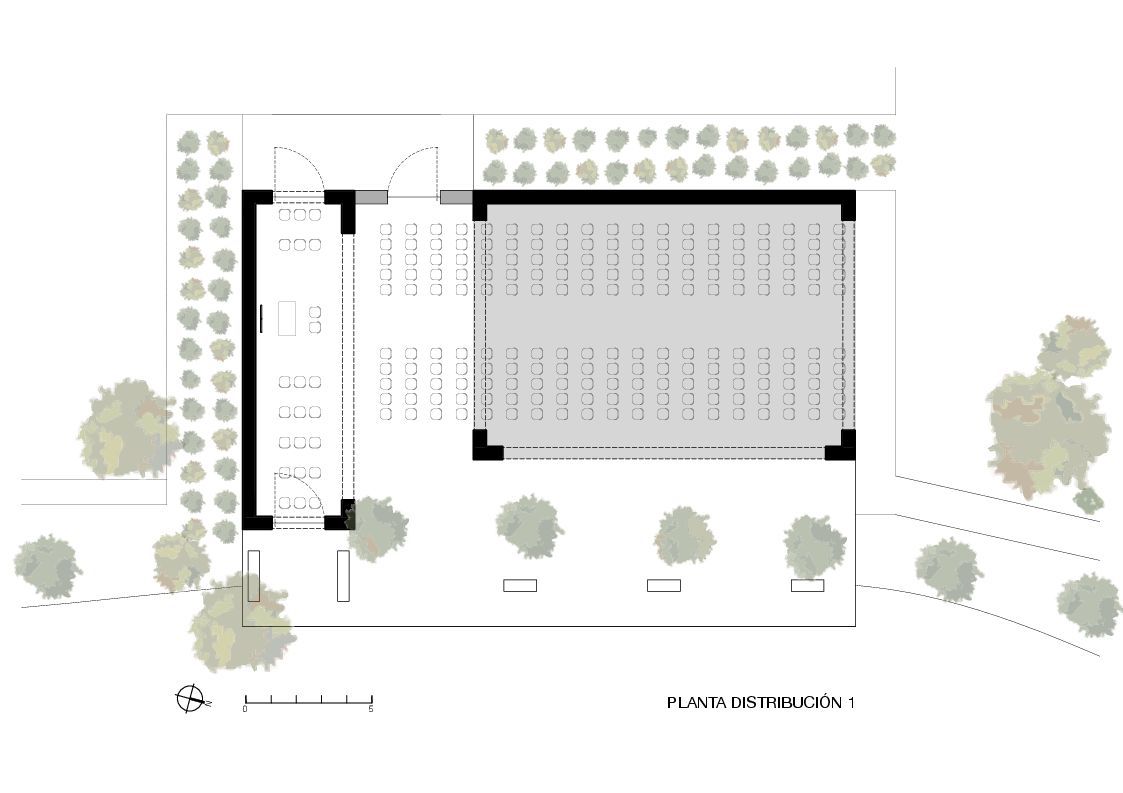 This chapel project was reimagined inside a tequila factory, located in the northeast of the state of Jalisco. The region is known to be one of the most religious areas in the country. This spiritual and social space is a reinterpretation of the mixed use spaces that exist in older haciendas and houses of the region, where people used to have a chapel or oratory in their own houses, adjacent to the terraces and open covered spaces, where social and family events were commonly held.
This chapel project was reimagined inside a tequila factory, located in the northeast of the state of Jalisco. The region is known to be one of the most religious areas in the country. This spiritual and social space is a reinterpretation of the mixed use spaces that exist in older haciendas and houses of the region, where people used to have a chapel or oratory in their own houses, adjacent to the terraces and open covered spaces, where social and family events were commonly held.
The team notes that the chapel sits on a cantilevered platform, overviewing the lake, the gardens, the factory and the agave fields. The plan drawing shows how the building is oriented in a way that its closed walls face the southern and western sun, keeping privacy from the patio. A terracotta tile pathway leads visitors from the factory towards the chapel, allowing them to admire the scenery, and enjoy the walk around the lake and gardens, leading them finally into the complex.
Jojutla Central Gardens
By Estudio MMX, Jojutla de Juárez, Morelos, Mexico
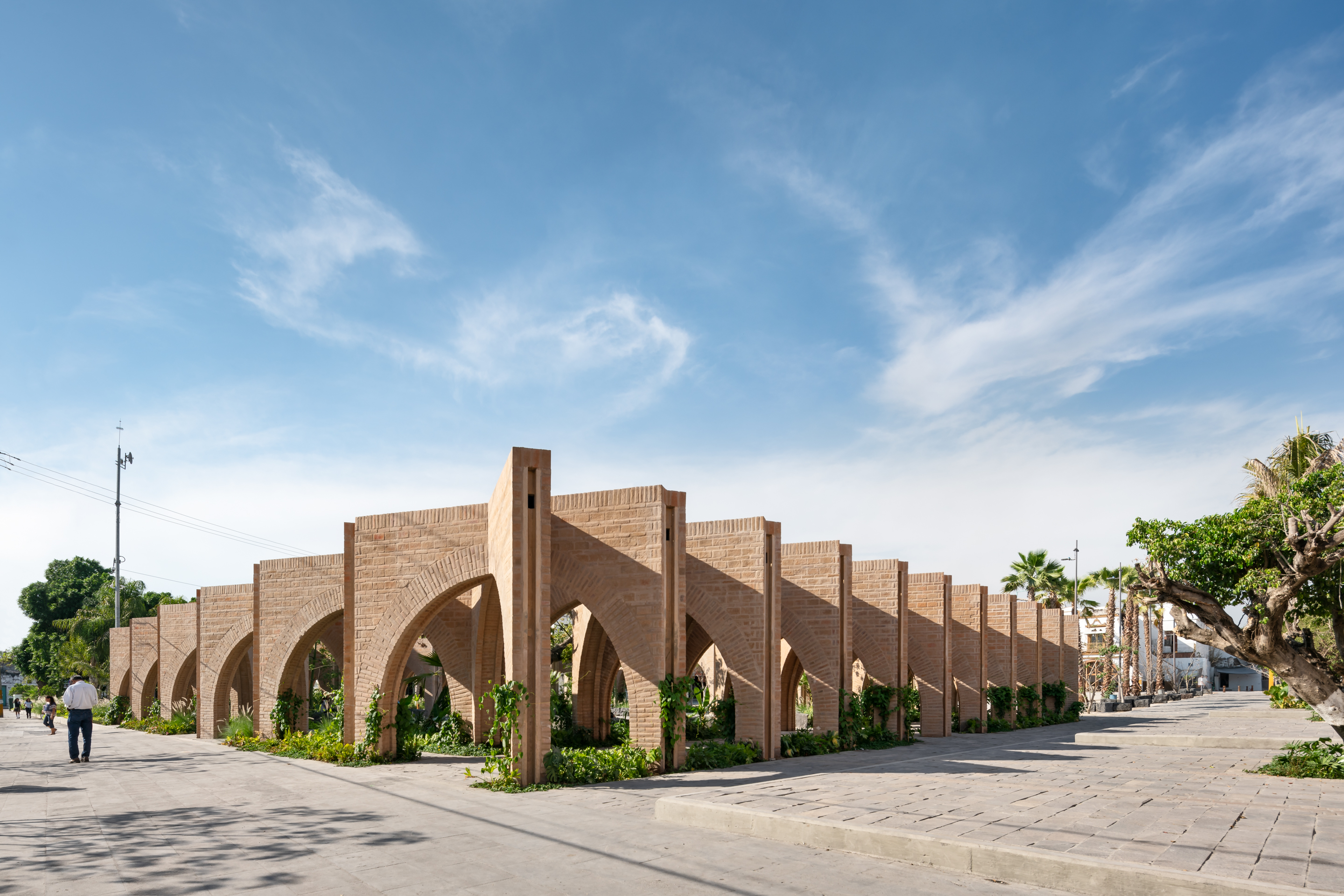
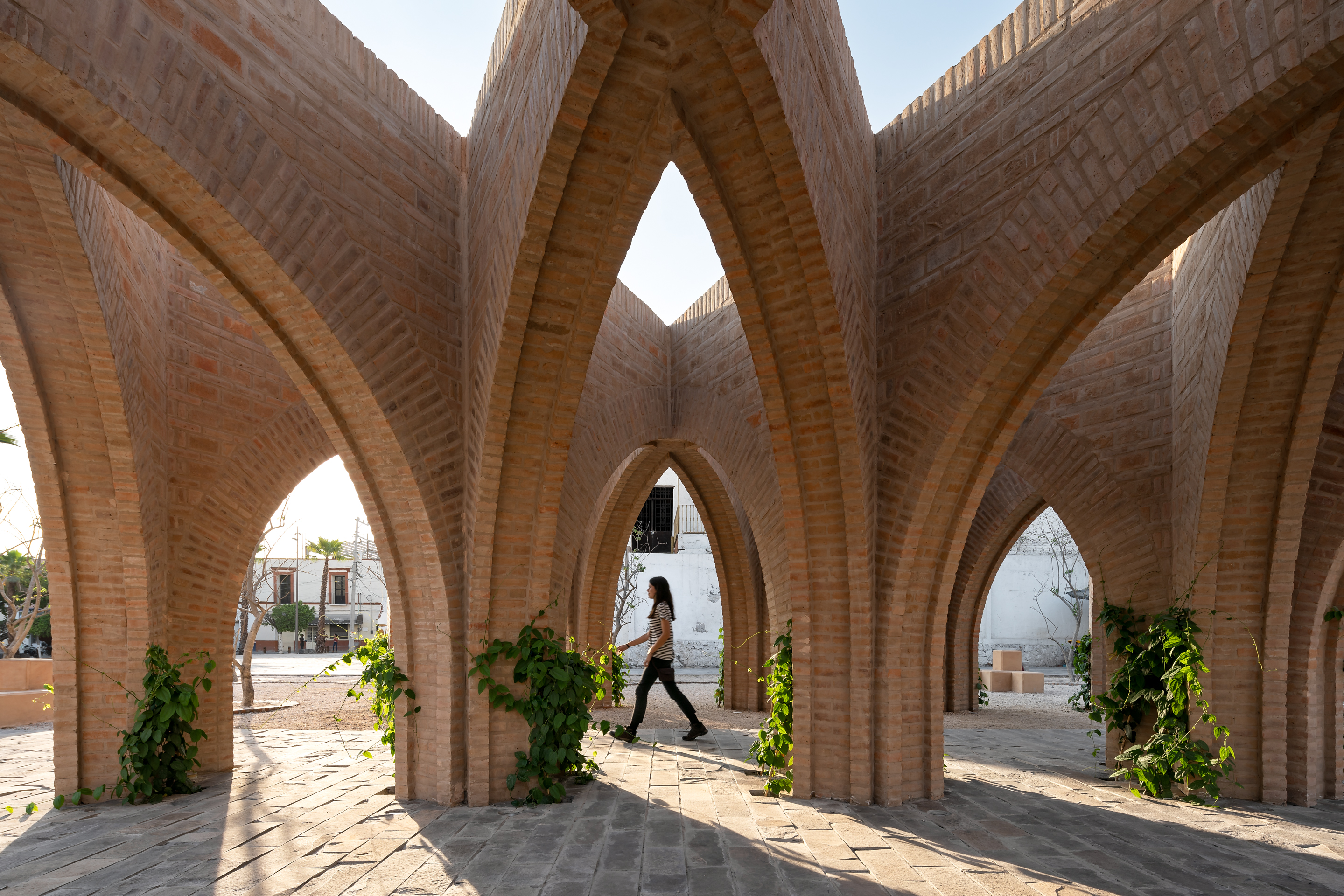


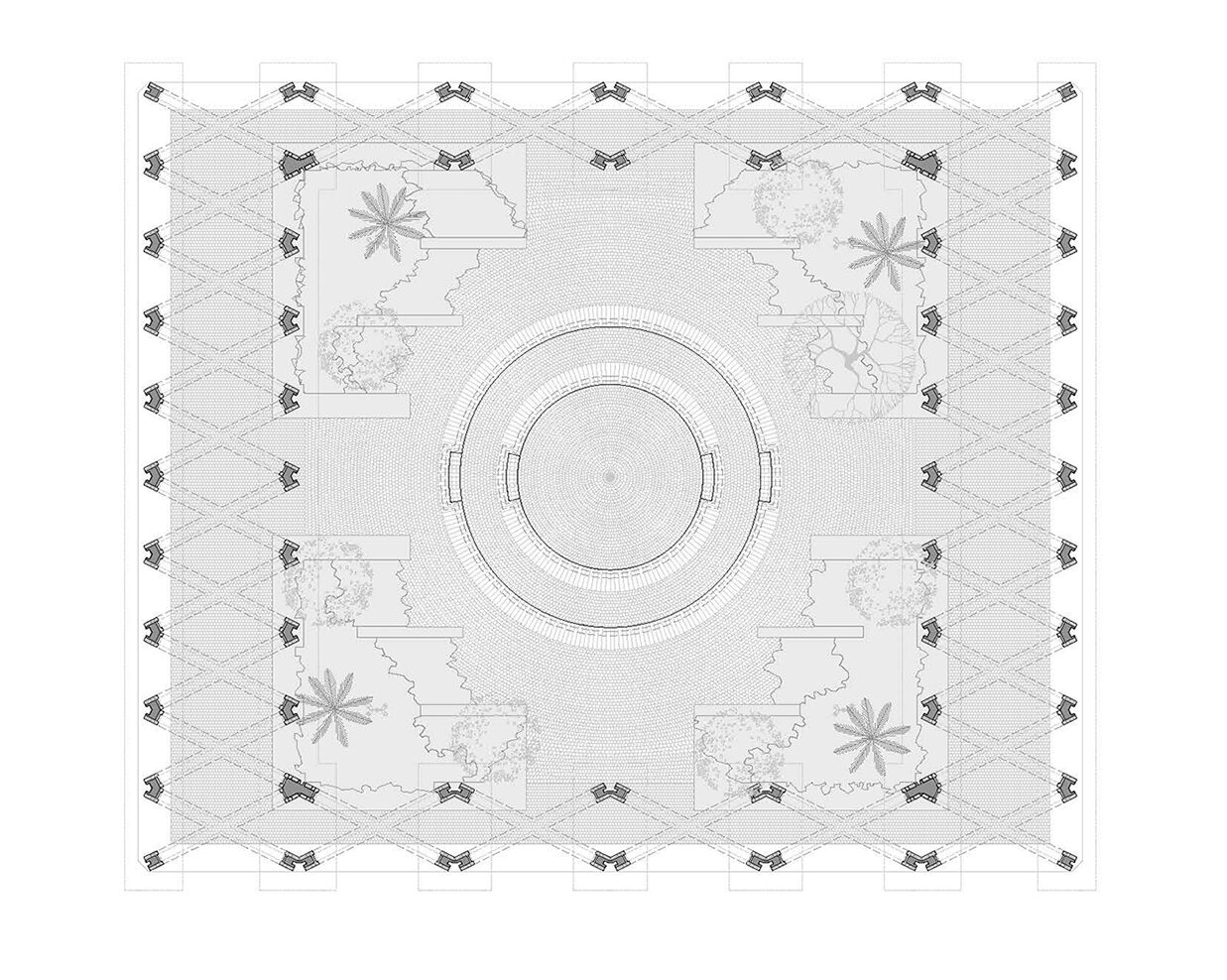 After devastating earthquakes in Mexico, this project was designed to rebuild an identity that uses public spaces as its media. At the heart of the design was a close interaction with the inhabitants of Jojutla. The core idea came from the trees. These unique elements survived the earthquakes without damage, therefore, the Civic Centre of Jojutla became the “Central Gardens of Jojutla” evoking the concept of resiliency by means of the vegetation.
After devastating earthquakes in Mexico, this project was designed to rebuild an identity that uses public spaces as its media. At the heart of the design was a close interaction with the inhabitants of Jojutla. The core idea came from the trees. These unique elements survived the earthquakes without damage, therefore, the Civic Centre of Jojutla became the “Central Gardens of Jojutla” evoking the concept of resiliency by means of the vegetation.
As seen in plan, there are arcades that coexist next to the gardens. These structures reinterpret the region’s traditional architecture. They serve as frames for the civic and leisure events required by the city. The selected materials were artisanal ochre brick, basaltic grey stone for pavements, and an extensive array of local flora species. The result was the generation of a civic square with a new identity.
Architects: Want to have your project featured? Showcase your work through Architizer and sign up for our inspirational newsletters.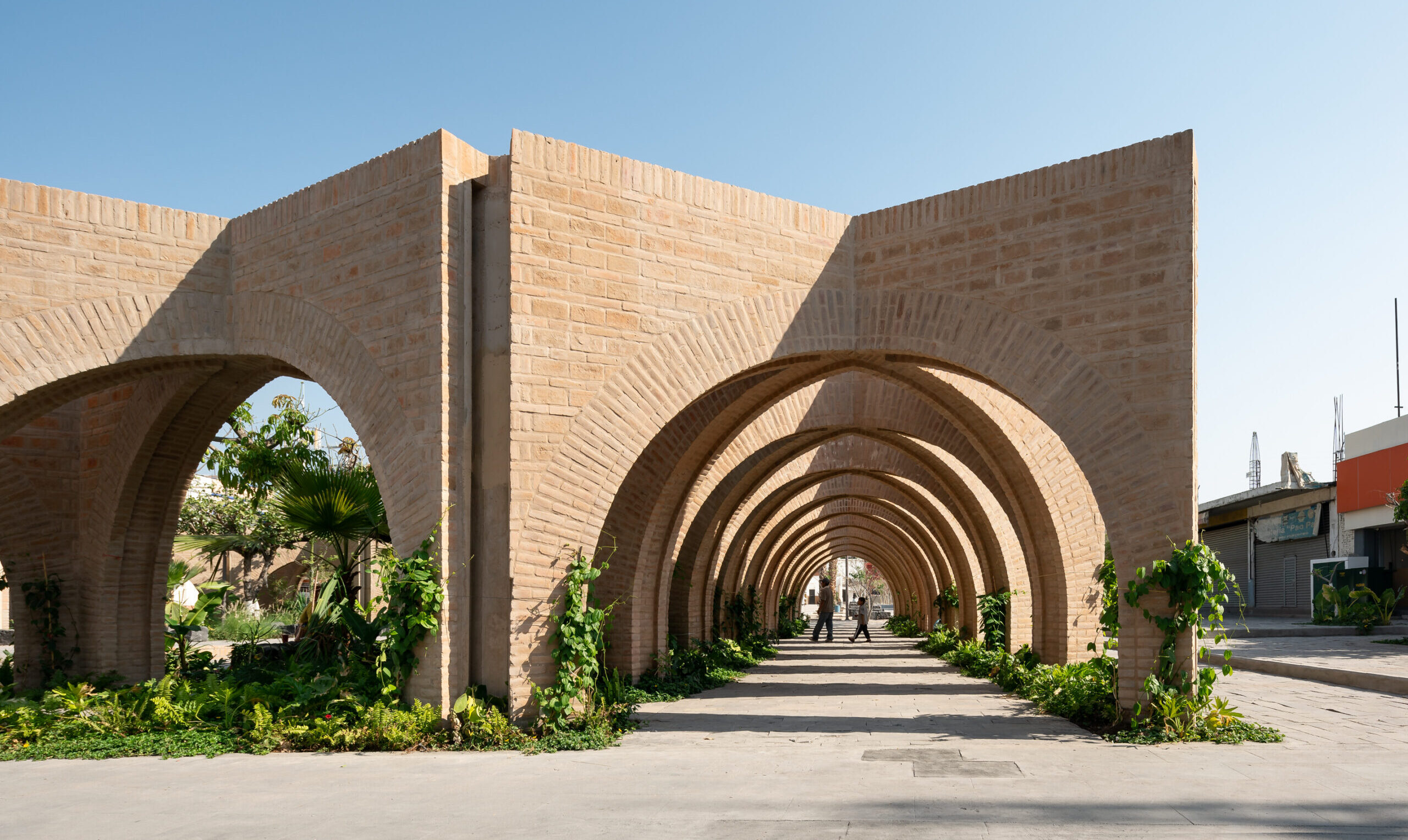





 Centinela Chapel
Centinela Chapel  Community Center San Bernabé
Community Center San Bernabé  Ecumenical Chapel
Ecumenical Chapel  Jojutla Central Gardens
Jojutla Central Gardens  Mar Adentro
Mar Adentro  Telcel Theater
Telcel Theater