We are thrilled to announce the winners of Architizer's inaugural Vision Awards, the world’s biggest awards program dedicated to the art of architectural representation. Sign up to receive future program updates >
Rendering transformed how architecture was visualized and shared. As one of the most common ways that designs are communicated to clients and the public today, these constructed images have become central to practice. Increasingly more realistic as technology has evolved, firms have been exploring diverse ways to understand the impact and potential of renderings. Now more than ever, designers and artists can make visualizations in less time and create new visions of what could be.
For interdisciplinary design practice Morphosis, the firm has made a name for itself by pushing boundaries. In their own words, the designers are “enthusiastically wondering at the future” as they test out new forms and building technologies. Founded in 1972, the firm’s work ranges in scale from residential, institutional, and civic buildings to large urban planning projects.
Like the practice itself and implied in the firm’s name, the renderings produced by Morphosis have shifted and evolved over time. However, a central theme is a blurred entourage and context, creating a sense of movement within an image. The following projects showcase renderings from the firm’s portfolio and photography of their built architecture. As a collection, they show how the practice continues to set the stage for innovation.
Orange County Museum of Art
Costa Mesa, CA, United States
Jury Winner, 2023 A+Awards, Museum
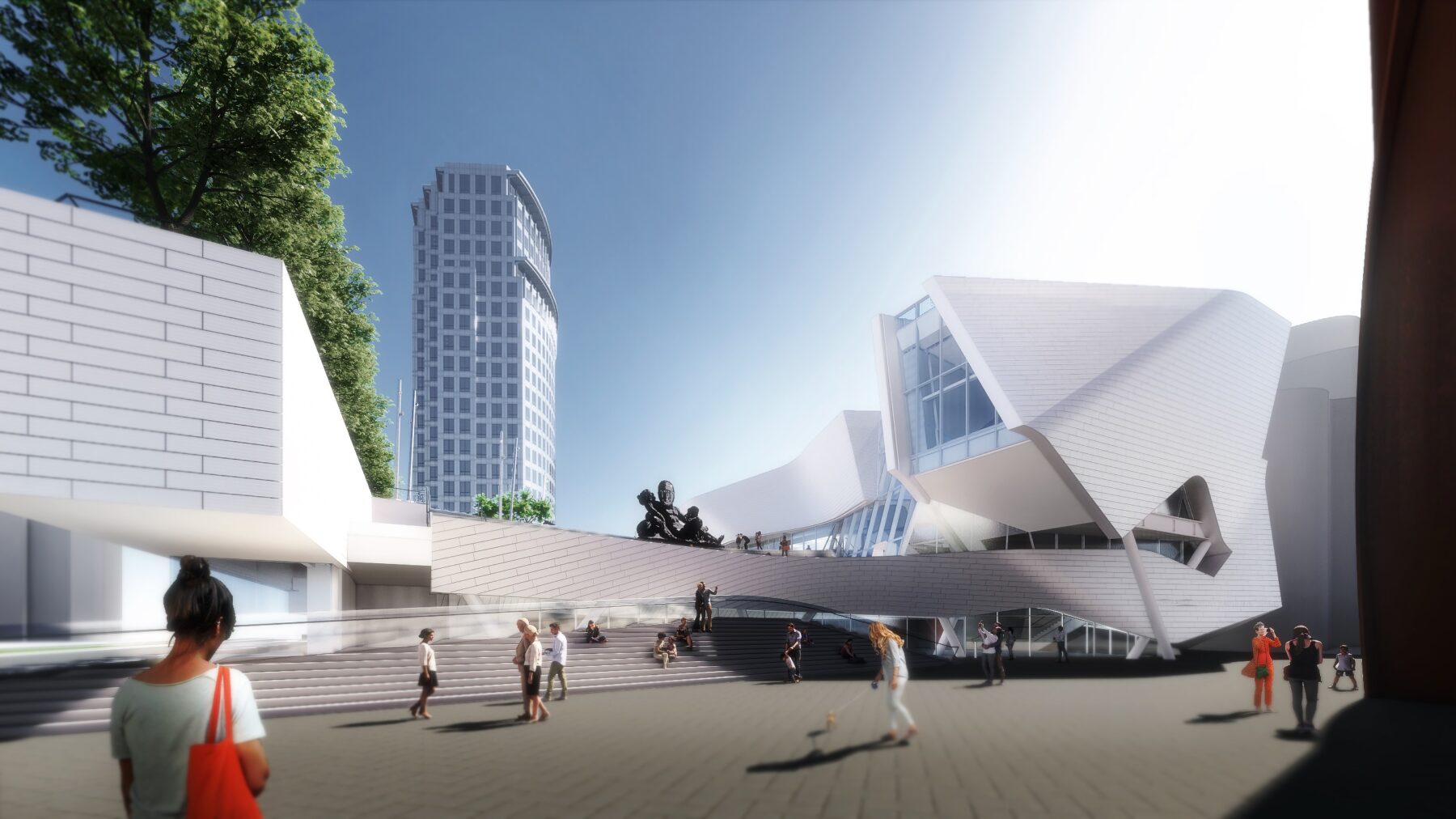
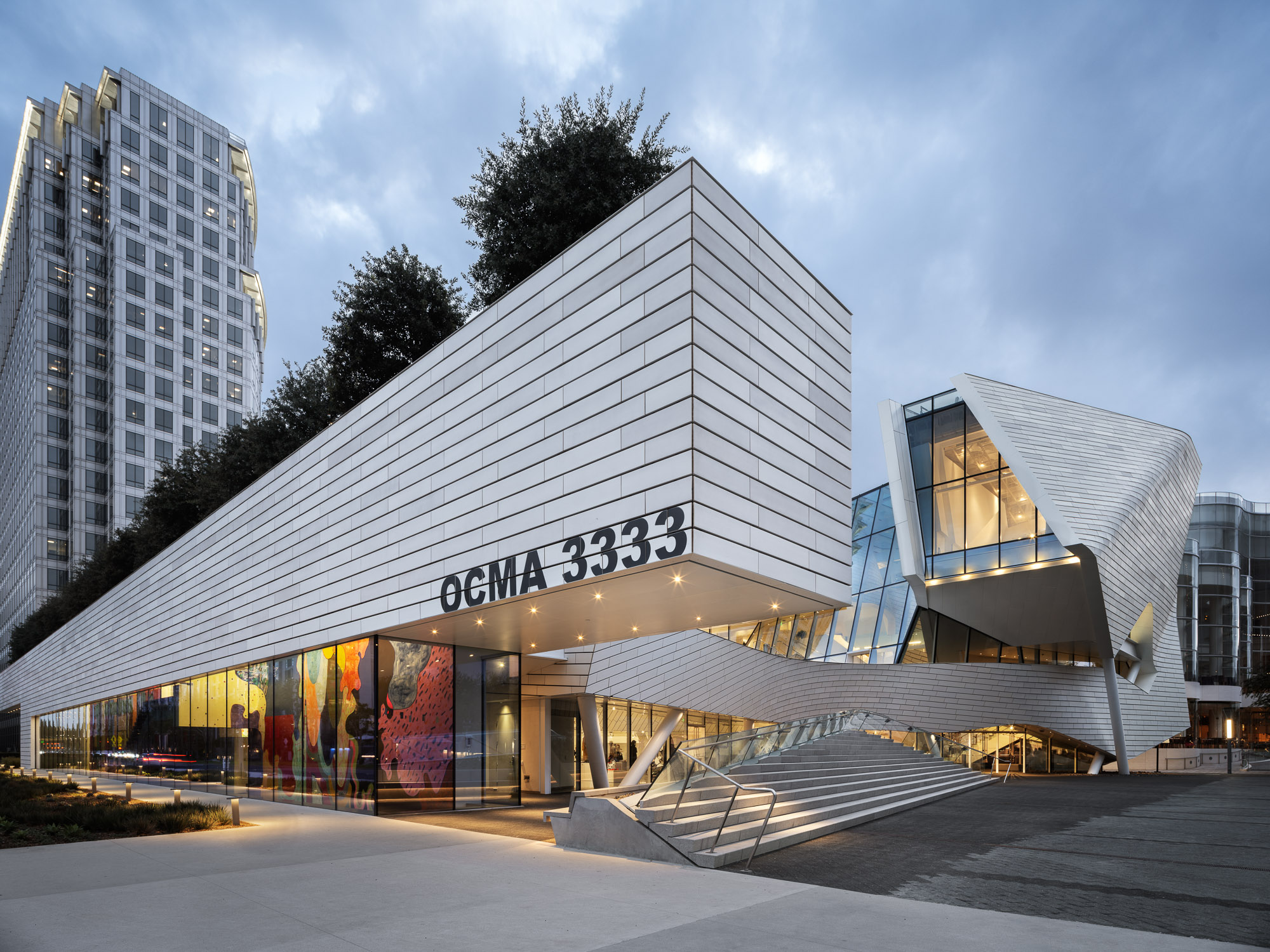
 The design of the new Orange County Museum of Art addresses the need for museum space to be both flexible and functional as well as inviting and memorable. With flexible exhibition galleries, dedicated space for educational programming, and areas for public gathering, the new building was made to provide expanded access to the museum’s permanent collection and its world-class special exhibition program. The main floor is dedicated to reconfigurable open-span exhibition space, complemented by mezzanine, black-box, and jewel-box galleries that can accommodate temporary and permanent collection exhibitions spanning scales and mediums.
The design of the new Orange County Museum of Art addresses the need for museum space to be both flexible and functional as well as inviting and memorable. With flexible exhibition galleries, dedicated space for educational programming, and areas for public gathering, the new building was made to provide expanded access to the museum’s permanent collection and its world-class special exhibition program. The main floor is dedicated to reconfigurable open-span exhibition space, complemented by mezzanine, black-box, and jewel-box galleries that can accommodate temporary and permanent collection exhibitions spanning scales and mediums.
A spacious roof terrace, equivalent in size to 70 percent of the building’s footprint, serves as an extension of the galleries with open-air spaces that can be configured for installations, a sculpture garden, outdoor film screenings, or events. While the interaction and entrance to this terrace changed over the course of the design, later renderings more closely echo the final project. A sculptural wing hovers over the lobby atrium and creates a prominent location for the educational hall, a dynamic architectural space illuminated by a full-height window overlooking the terrace.
Perot Museum of Nature and Science
Dallas, TX, United States
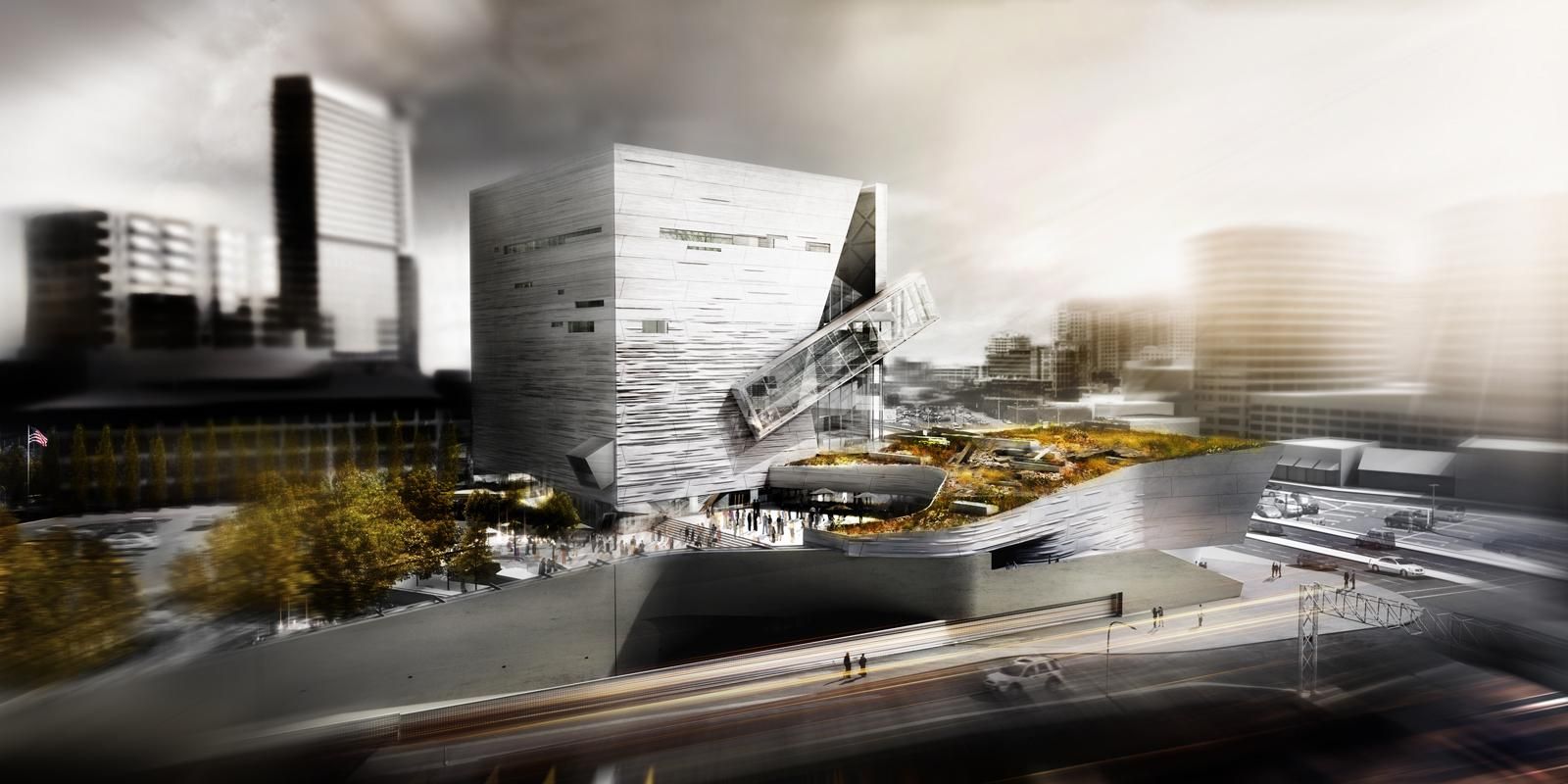
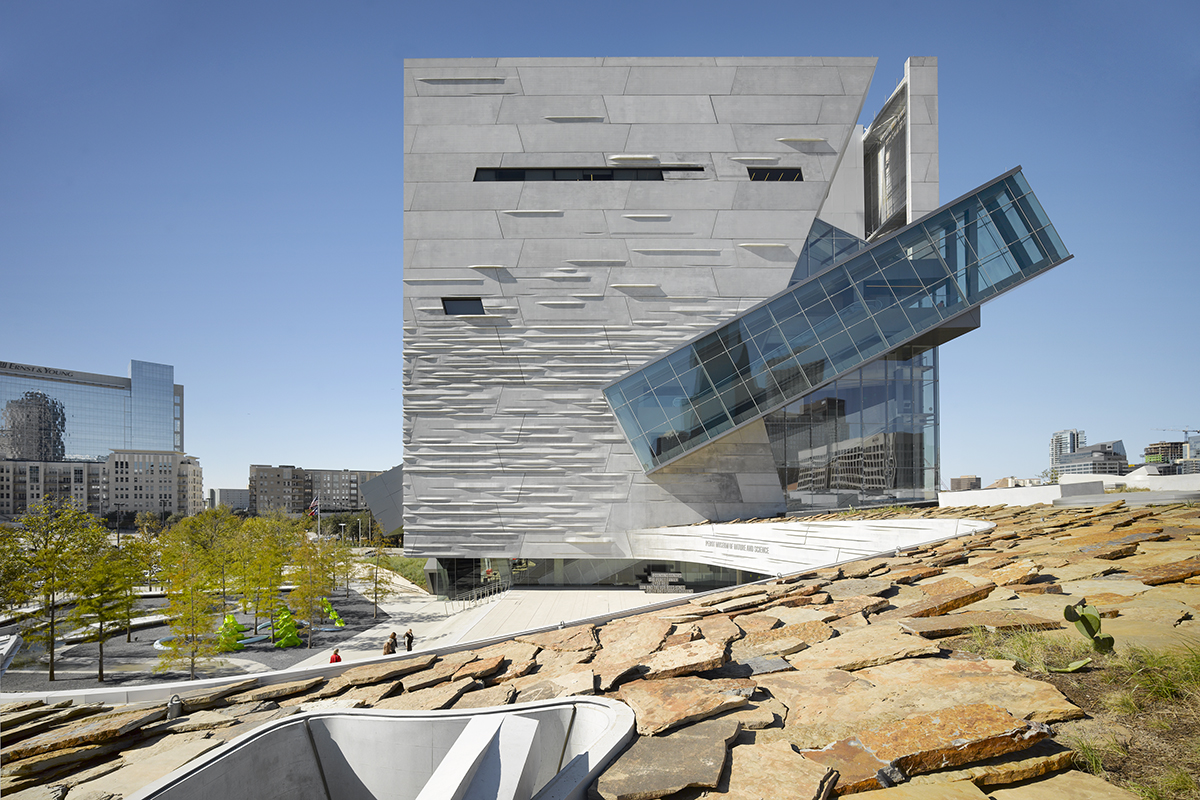
 Giving shape to concrete, Morphosis Architects explored the material’s potential through the Perot Museum of Nature and Science in Dallas. Built to bring a simple cube and plinth into high relief, the Perot Museum showcases a precast-concrete panel façade. As a material investigation integrating structure and formwork, the elegant cladding solution was made possible through computer aided modeling and a collaboration with Gate Precast of Hillsboro, Texas.
Giving shape to concrete, Morphosis Architects explored the material’s potential through the Perot Museum of Nature and Science in Dallas. Built to bring a simple cube and plinth into high relief, the Perot Museum showcases a precast-concrete panel façade. As a material investigation integrating structure and formwork, the elegant cladding solution was made possible through computer aided modeling and a collaboration with Gate Precast of Hillsboro, Texas.
The Perot Museum is a showcase of versatility and technical ability. Its design creates a distinct identity for the new institution and enriches the urban environment of the emerging cultural district of Victory Park. The overall massing for the building floats a cube of galleries above a thickened landscape containing classrooms, a theater and support spaces. Breaking the solid geometry of the museum cube, a glass-encased 54-foot (16-meter) continuous flow escalator moves patrons up from the ground floor to a cantilevered platform, which is seen in both renderings of the project and the completed building.
Bloomberg Center
New York, NY, United States
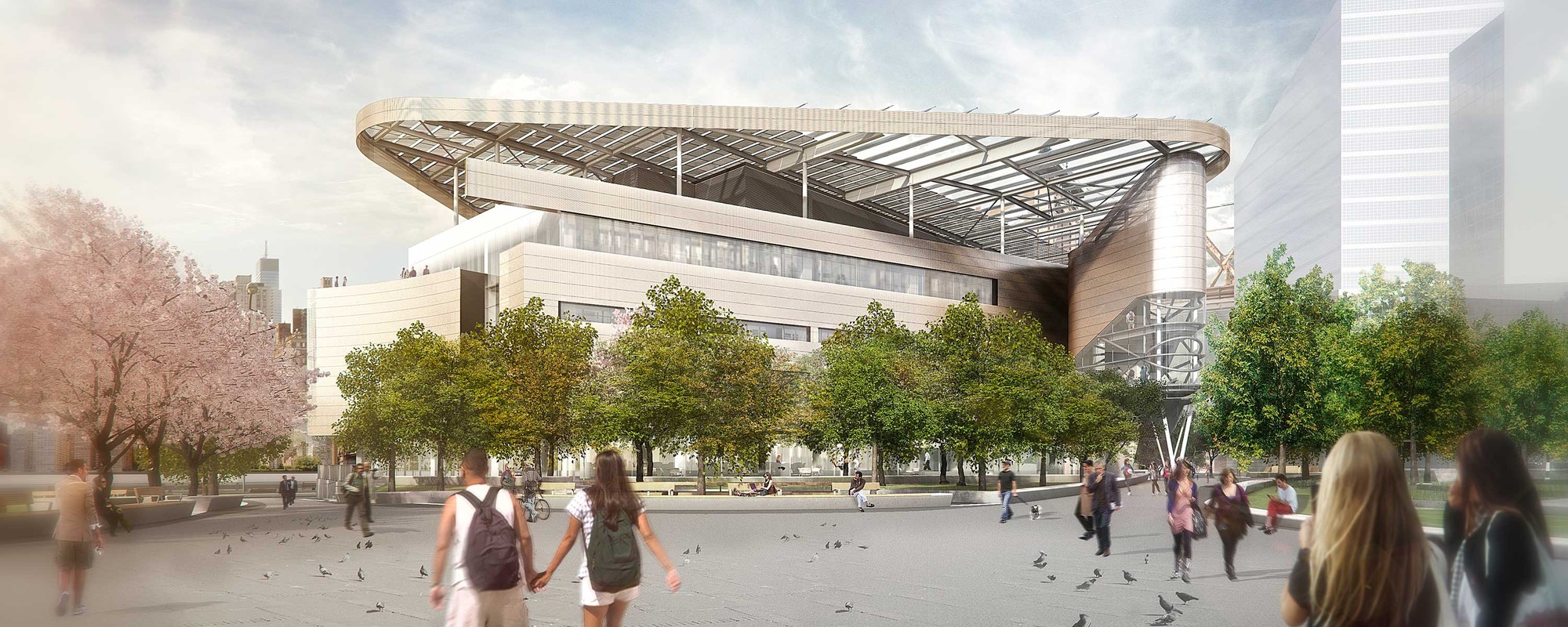
 Designed to become a net-zero building, The Bloomberg Center forms the heart of the Cornell Tech campus on Roosevelt Island. The Bloomberg Center was made to reflect the school’s joint goals of creativity and excellence by providing academic spaces that foster collective enterprise and collaboration. The four-story, 160,000-square-foot (14,865-square-meter) academic building is named in honor of Emma and Georgina Bloomberg in recognition of a $100-million gift from Michael Bloomberg, who was responsible for bringing Cornell Tech to New York City while serving as the city’s 108th Mayor. The four-story building is set beneath a photovoltaic canopy with a low and narrow profile framing views across the island.
Designed to become a net-zero building, The Bloomberg Center forms the heart of the Cornell Tech campus on Roosevelt Island. The Bloomberg Center was made to reflect the school’s joint goals of creativity and excellence by providing academic spaces that foster collective enterprise and collaboration. The four-story, 160,000-square-foot (14,865-square-meter) academic building is named in honor of Emma and Georgina Bloomberg in recognition of a $100-million gift from Michael Bloomberg, who was responsible for bringing Cornell Tech to New York City while serving as the city’s 108th Mayor. The four-story building is set beneath a photovoltaic canopy with a low and narrow profile framing views across the island.
One of the building’s most distinctive features is its façade, optimized to balance transparency — optimizing daylighting and exterior views — while maximizing insulation and reducing thermal bridging. As the renderings echo the building’s form, they also hint at this texture created along the building facade. Designed as a rain screen system, the outermost layer of the façade is composed of aluminum panels surfaced in an iridescent, PPG polymer coating. Viewed from afar, the aluminum panels register a continuous image that merges the river-view scenery from Cornell Tech’s Roosevelt Island location and Cornell University’s idyllic campus in Ithaca, New York.
Emerson Los Angeles
Los Angeles, CA, United States
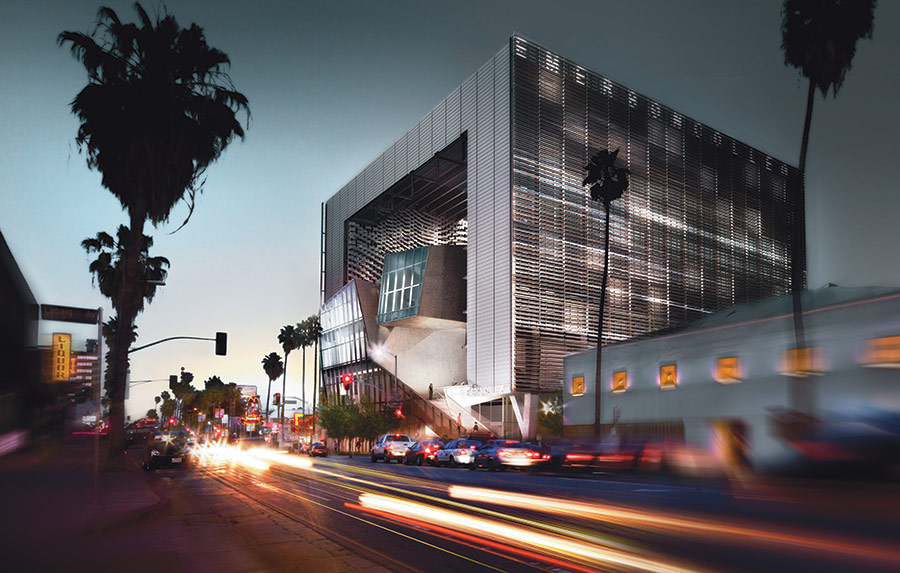
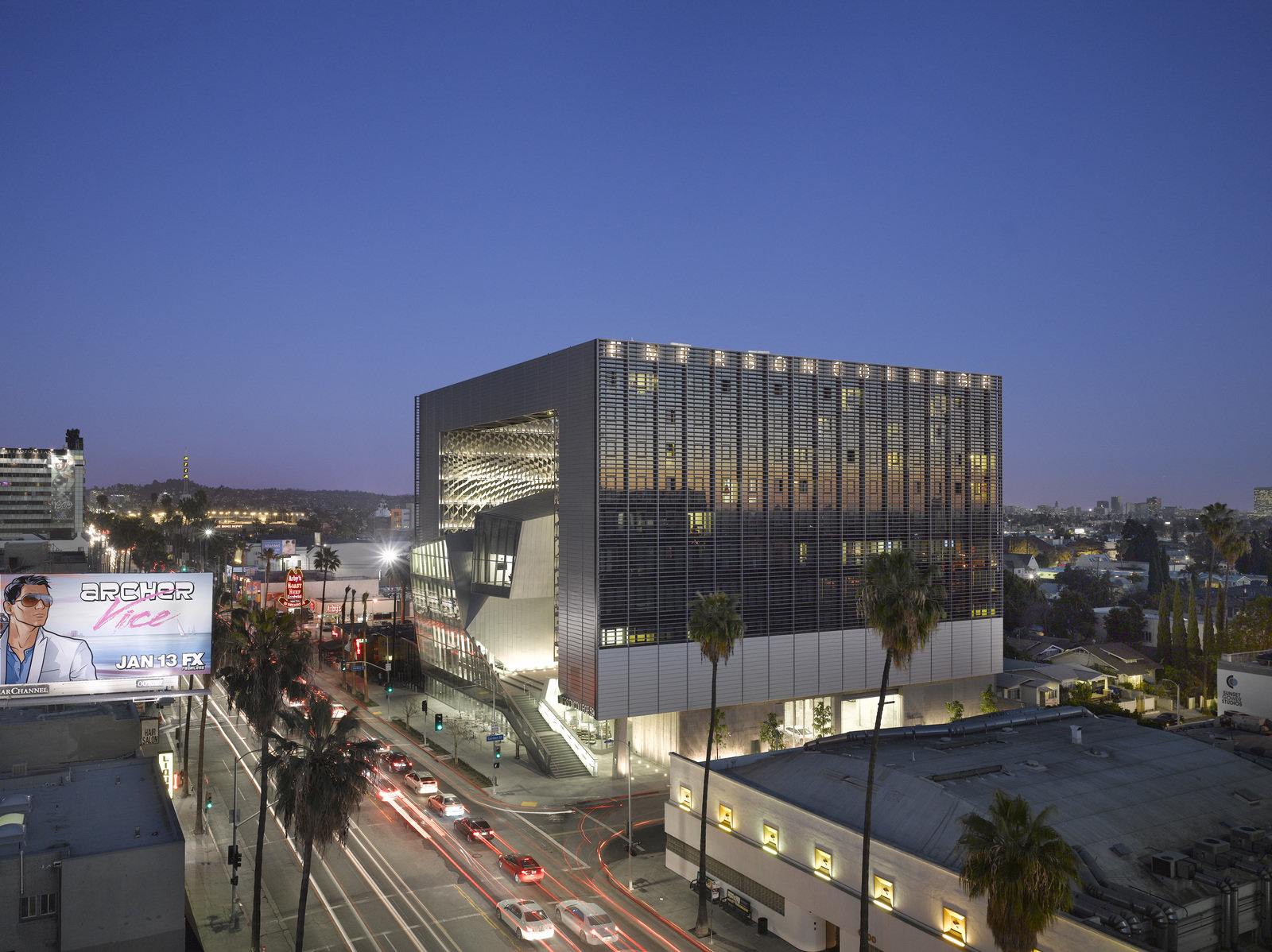
 Emerson Los Angeles has emerged as a significant landmark in Los Angeles. As a backdrop for student filmmakers, the building weaves an urban fabric of outdoor and indoor spaces together with two slender residential towers bridged by a multi-use platform. With over 180 student rooms, four faculty apartments, film and video production labs, and classrooms, the project combines both a sculptural central mass and an undulating, textured metal scrim. At over 100,000 square feet (9,290 square meters) and ten stories high, the project spurred redevelopment as part of a larger transformation in Hollywood.
Emerson Los Angeles has emerged as a significant landmark in Los Angeles. As a backdrop for student filmmakers, the building weaves an urban fabric of outdoor and indoor spaces together with two slender residential towers bridged by a multi-use platform. With over 180 student rooms, four faculty apartments, film and video production labs, and classrooms, the project combines both a sculptural central mass and an undulating, textured metal scrim. At over 100,000 square feet (9,290 square meters) and ten stories high, the project spurred redevelopment as part of a larger transformation in Hollywood.
As the most distinctive element of the project, the building features a custom metal panel systems manufactured by Zahner. These screens and panels were made to provide shade and privacy, and are composed of seventeen different folded aluminum components. This screen is seen in both renderings of the design, as well as in the heart of the finished building. Zahner used 3D models to produce and fabricate the curvatures. The eight-story sunscreen was made using computational scripting to determine the final geometry that would shade the internal façades.
Kolon One & Only Tower
Gangseo-gu, Seoul, South Korea
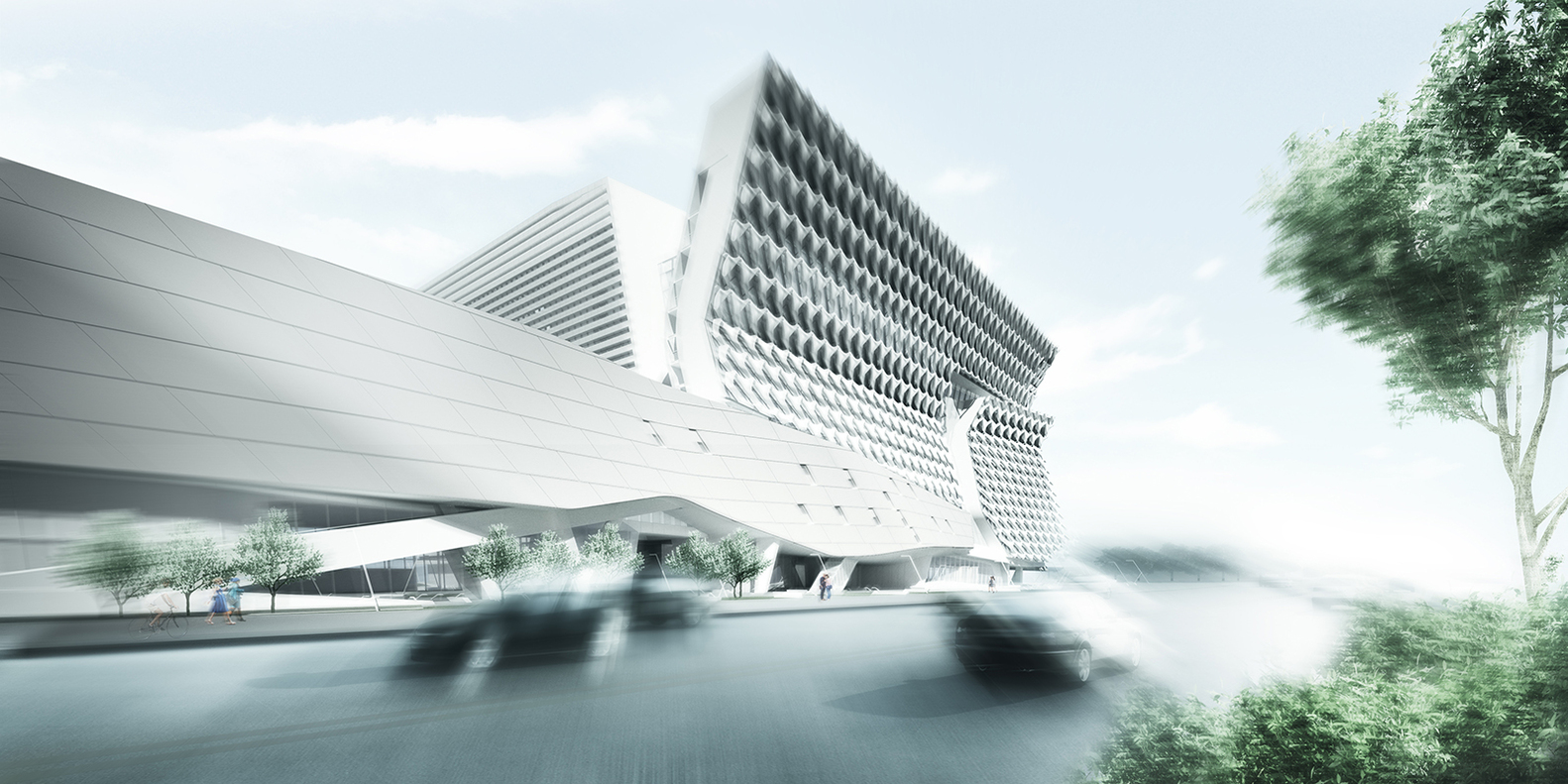
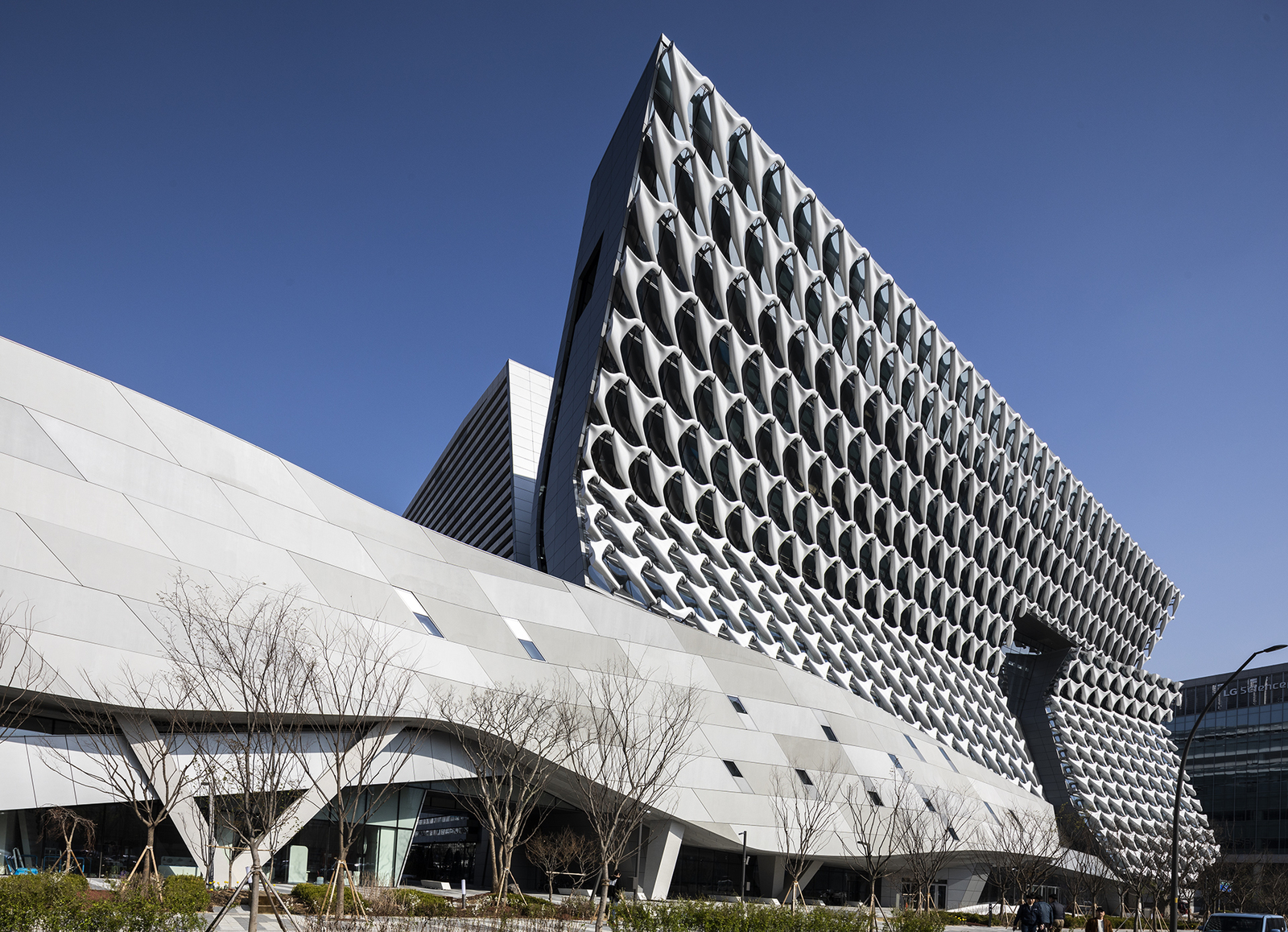
 Sited in Seoul, Kolon’s new flagship research and development facility brings together researchers, leadership and designers in one location. The building combines flexible laboratory facilities with executive offices and active social spaces that encourage greater interaction and exchange across the company. The four-acre project site sits adjacent to Magok’s central park — a prominent location for what will be the district’s first major completed building. The building folds towards the park, providing passive shading to the lower floors.
Sited in Seoul, Kolon’s new flagship research and development facility brings together researchers, leadership and designers in one location. The building combines flexible laboratory facilities with executive offices and active social spaces that encourage greater interaction and exchange across the company. The four-acre project site sits adjacent to Magok’s central park — a prominent location for what will be the district’s first major completed building. The building folds towards the park, providing passive shading to the lower floors.
Bridging the three extending laboratory wings, the building’s folding volume contains conference rooms and social spaces, augmented by flagship retail and exhibition galleries at the street level to communicate the brand’s vision to the public. A transparent ground plane extends the landscape into the interior, drawing light and movement towards an open pedestrian lane-way and grand entry. The distinctive brise-soleil system on the western façade is both a performative and symbolic feature of the building; the façade units have been parametrically shaped to balance shading and views, and are made from a GFRP formulation that uses one of Kolon’s own high-tech fabrics.
Gates Hall
Ithaca, NY, United States
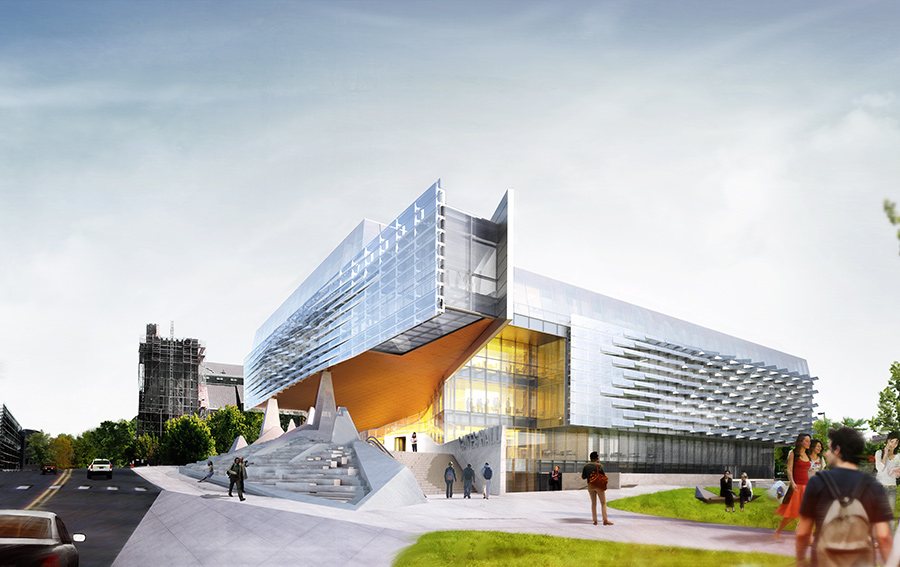
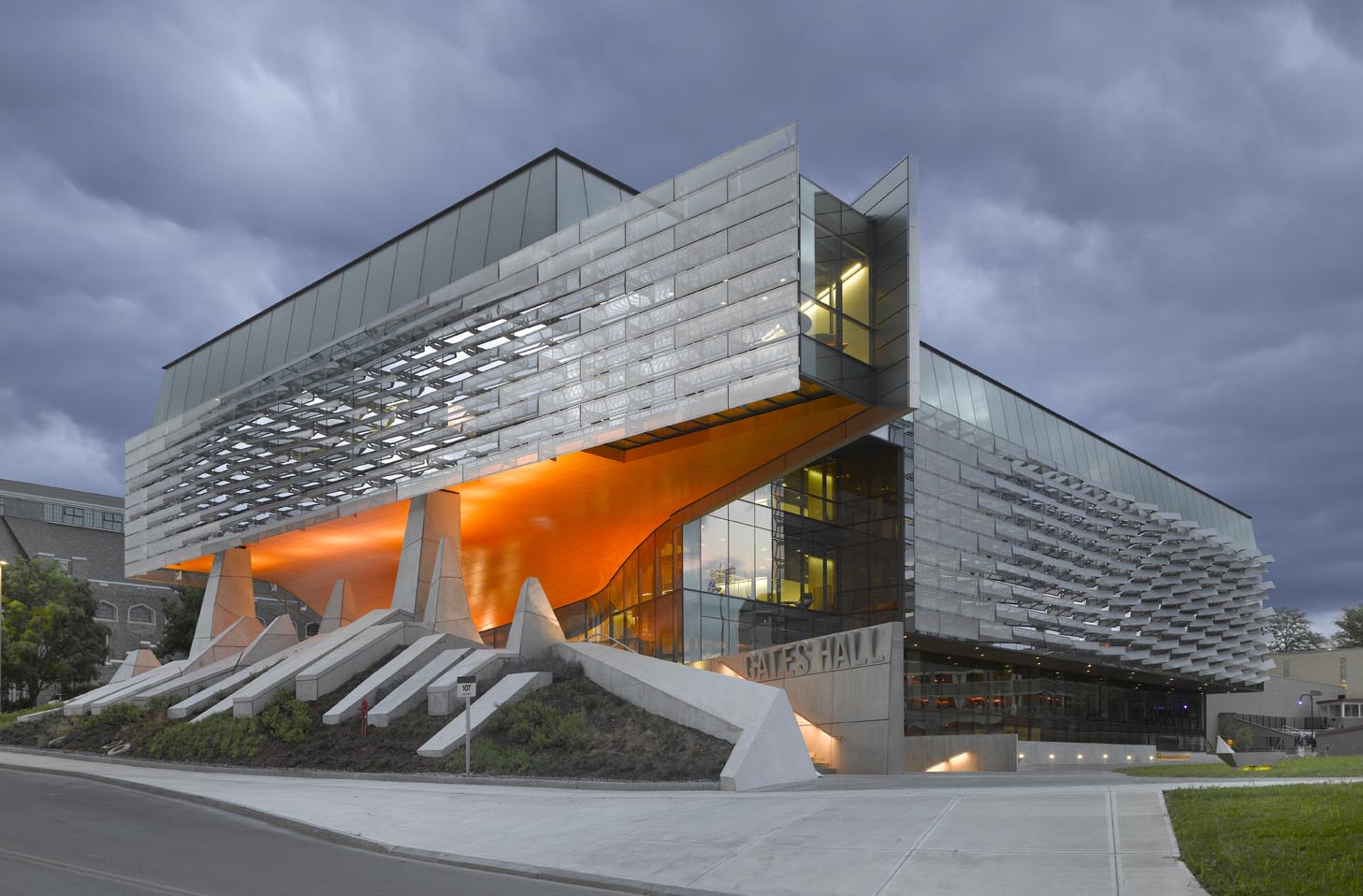
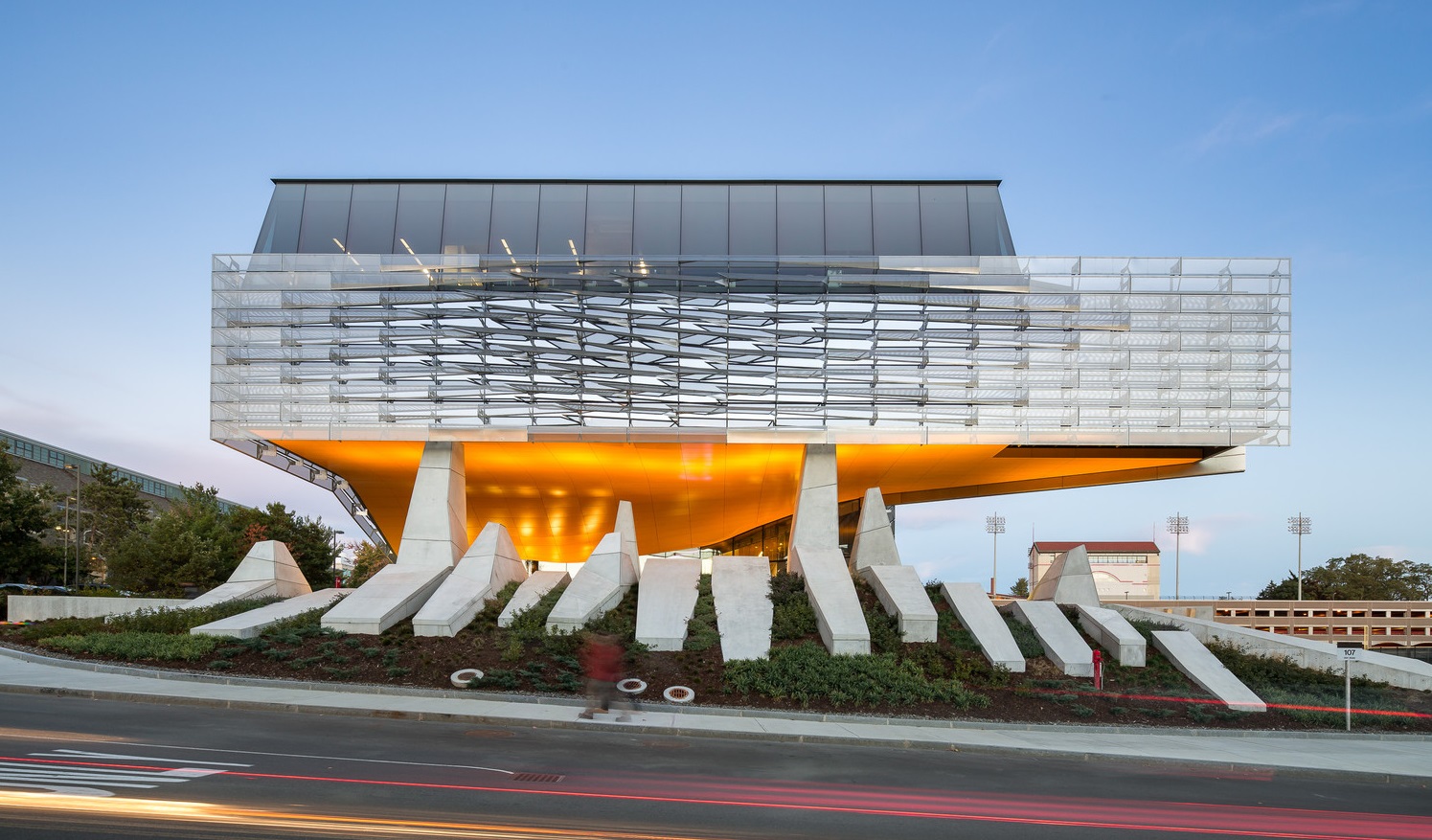
 The Bill & Melinda Gates Hall brings together the faculty and students of Cornell University’s Computer Science and Information Science departments. Housed within a single structure, the project was designed to facilitate collaboration and spontaneous discourse between disciplines. Projecting westward from the building, a two-story cantilever creates a dramatic canopy over the elevated Entry Plaza to establish a new visual gateway to the campus. Advanced digital modeling tools are used to map a double skin of undulating, perforated stainless steel panels, which envelop the reflective glass curtain wall on the second and third levels.
The Bill & Melinda Gates Hall brings together the faculty and students of Cornell University’s Computer Science and Information Science departments. Housed within a single structure, the project was designed to facilitate collaboration and spontaneous discourse between disciplines. Projecting westward from the building, a two-story cantilever creates a dramatic canopy over the elevated Entry Plaza to establish a new visual gateway to the campus. Advanced digital modeling tools are used to map a double skin of undulating, perforated stainless steel panels, which envelop the reflective glass curtain wall on the second and third levels.
The complex patterning of the façade causes the building to appear to shift throughout the day, evening and seasons, as the sun reflects off this textural surface. The renderings of the project produced for Cornell echo the final design. Performative as well as aesthetic, the metal screen shades the building from the sun, while admitting diffuse daylight and affording exterior views. Accentuated by fritted interior glazing, active social spaces interweave with academic program to extend education beyond traditional classroom settings. Public activity is organized around a dynamic, multi-level atrium on the west side of the building, with an efficient layout of classroom, laboratories and offices to the east.
We are thrilled to announce the winners of Architizer's inaugural Vision Awards, the world’s biggest awards program dedicated to the art of architectural representation. Sign up to receive future program updates >





 Bloomberg Center
Bloomberg Center  Gates Hall
Gates Hall  Perot Museum of Nature and Science
Perot Museum of Nature and Science 


