The judging process for Architizer's 12th Annual A+Awards is now away. Subscribe to our Awards Newsletter to receive updates about Public Voting, and stay tuned for winners announcements later this spring.
In the ever-evolving landscape of urban design, the emergence of design districts has become a defining characteristic of progressive cities worldwide. These vibrant enclaves, often juxtaposed against the backdrop of industrial relics or purposefully planned developments, have become catalysts for economic growth, creative collaboration and community engagement.
At its core, a design district is a concentrated area within a city that serves as a thriving hub for creative and design-focused activities. These are places where architects, designers, artists and entrepreneurs converge to showcase their talents, exchange ideas and create an immersive experience for visitors. The value of a design district extends beyond its aesthetic allure; it breathes life into the local economy and community, fostering economic growth, cultural enrichment and a sense of place.
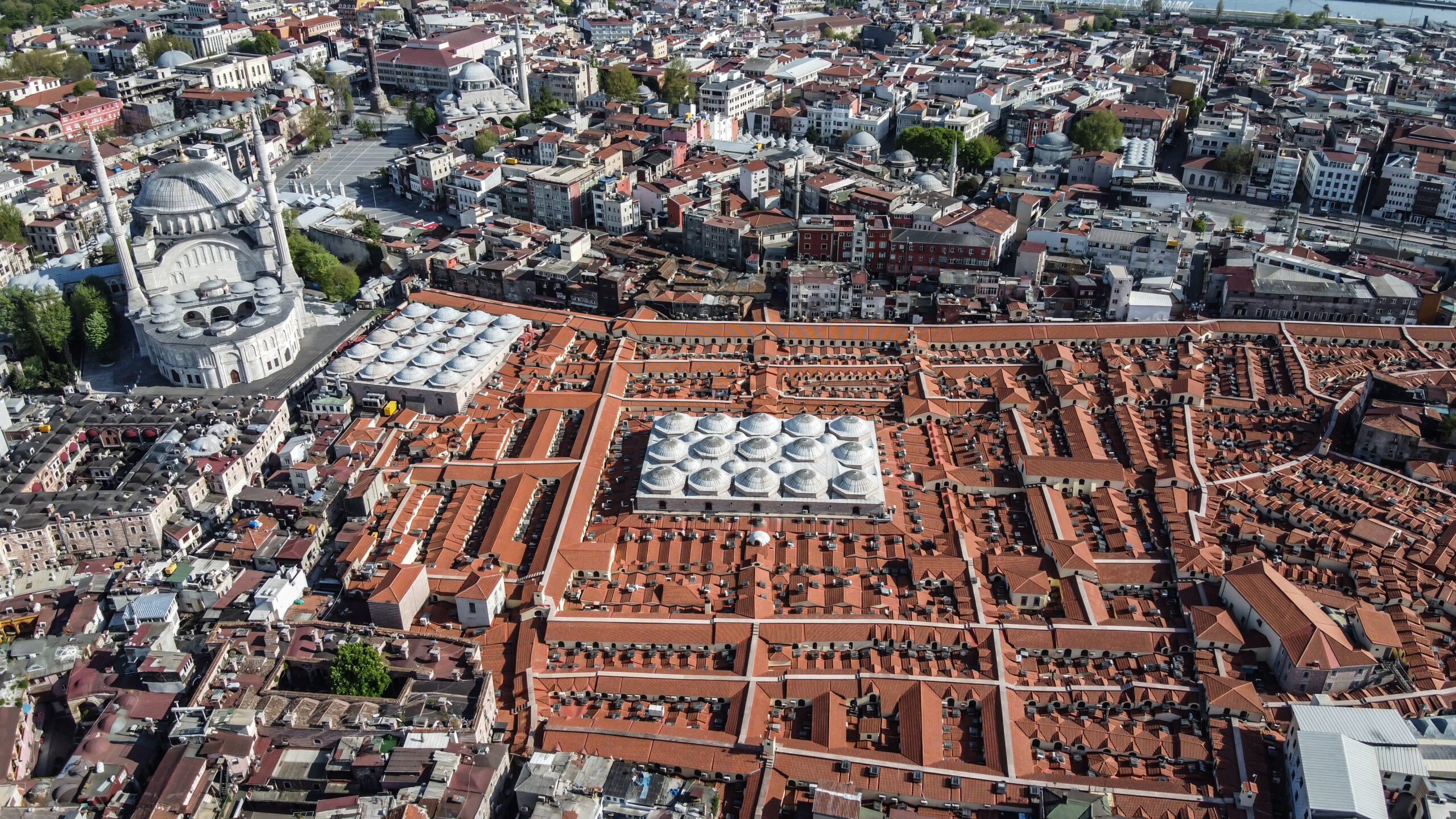

Grand Bazaar of Istanbul by IV. Murat
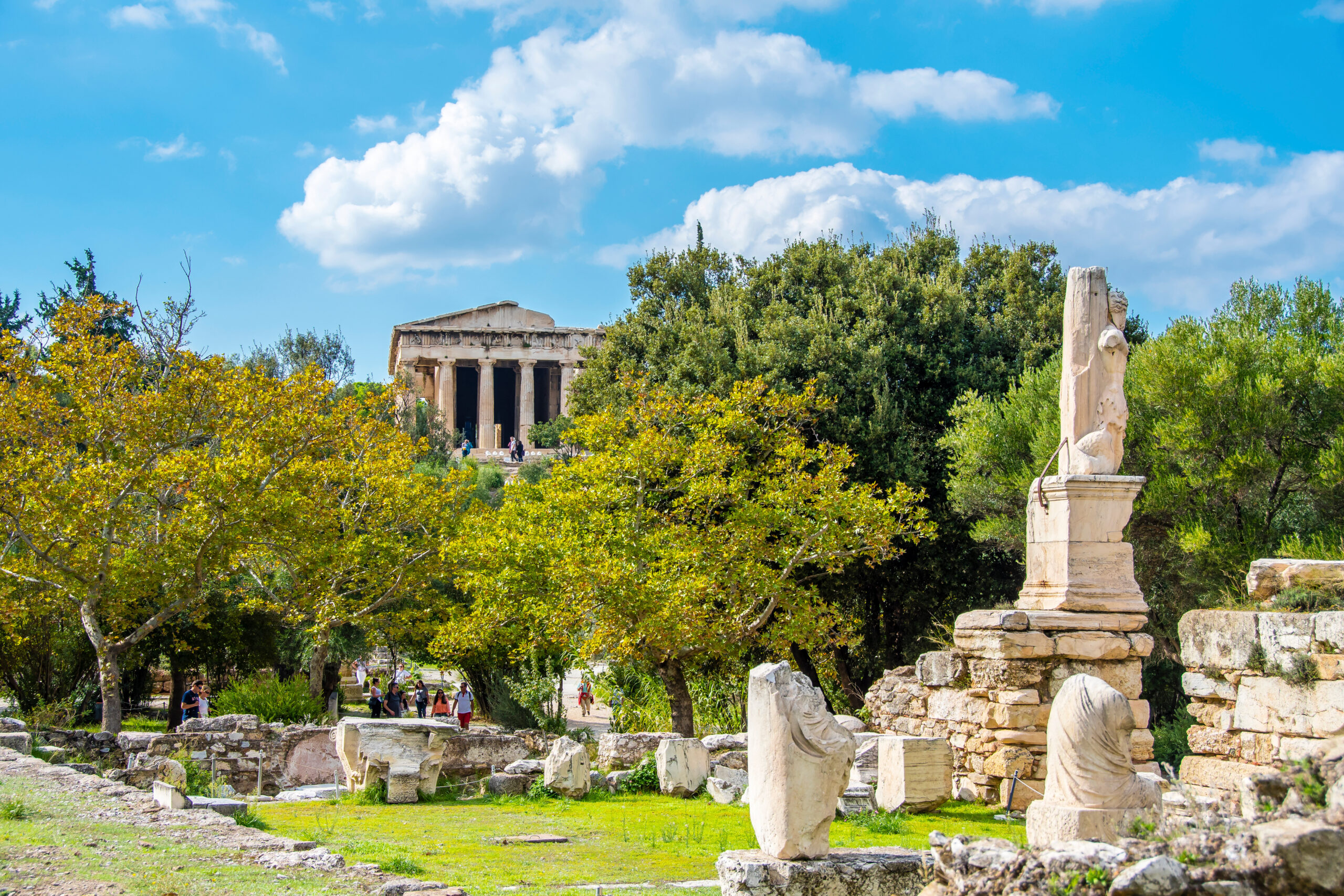
Long before the rise of modern metropolises, ancient civilizations laid the foundation for what we now recognize as design districts. These neighborhoods of artisans and craftspeople played a crucial role in the cultural and economic fabric of their respective societies. The Agora of Athens was a bustling marketplace that served as a hub for artists, philosophers and traders. Within its grand colonnades and stoa, the Agora fostered the exchange of ideas, the birth of democracy and the creation of iconic architectural wonders like the Parthenon.
While across the Aegean Sea, the 61 covered streets and 4,000 shops that make up the Grand Bazaar of Istanbul traces its origins back to the 15th century. This labyrinthine marketplace encapsulated the rich heritage and diverse influences of the Ottoman Empire. Within its alleyways, artisans, jewelers and carpet weavers transformed the Bazaar into a beacon of trade, attracting visitors from far and wide and establishing Istanbul as a global exchange hub.
Since then, we have borne witness to the emergence of many design districts across every continent and over centuries of design movements, and it was the demise of the industrial era that may have resulted in the most significant growth of the “design district.” Following the Second World War, countless factories and warehouses were left empty, creating opportunities for revitalization and adaptive reuse.
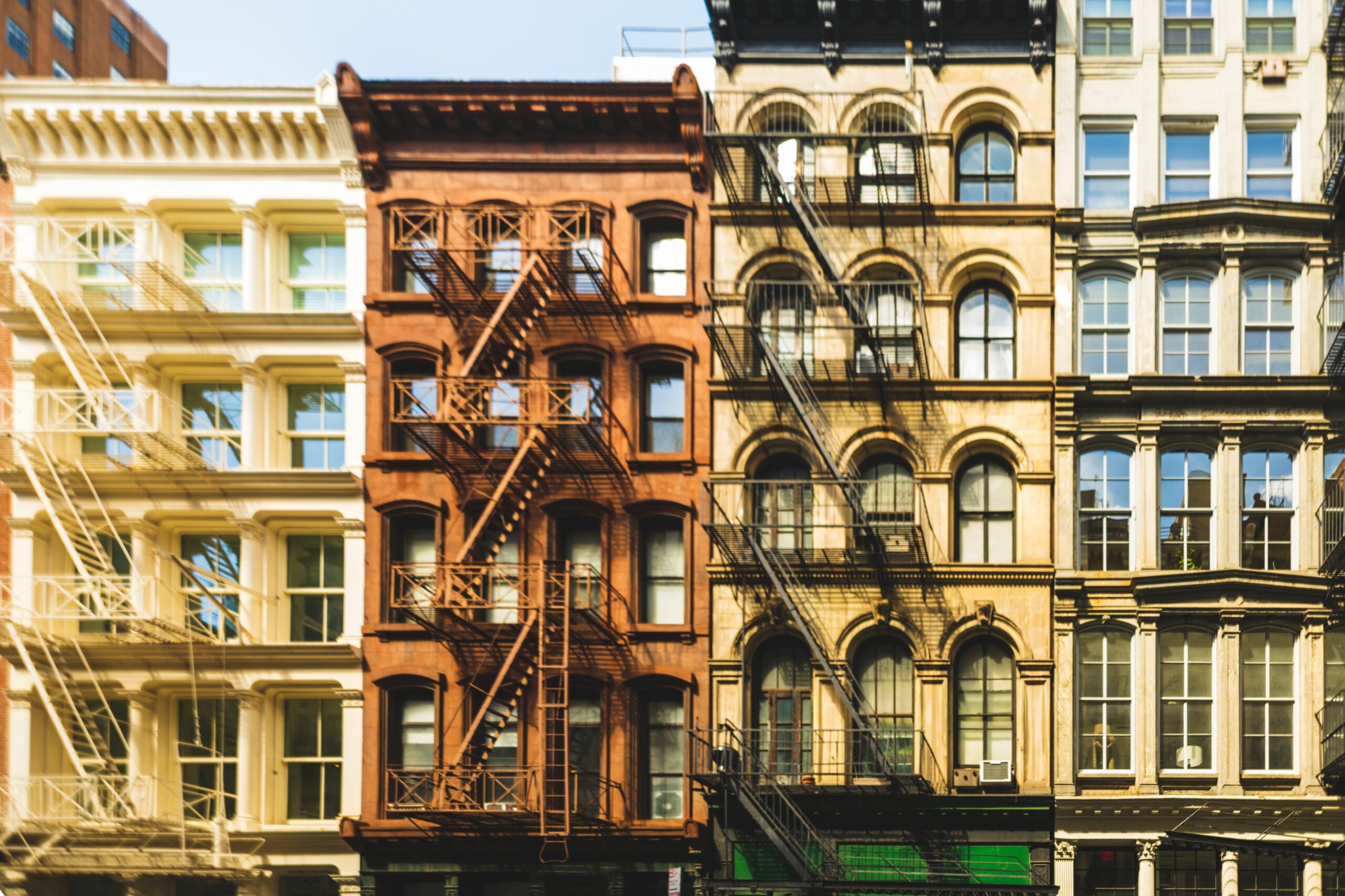

Soho neighborhood, Lower Manhattan, New York by Rafael Sanchez Lopez/Wirestock Creators
Starting with SoHo in New York City of the 1960s, abandoned factories and warehouses became fertile ground for architectural reinvention across the world. Once-decaying cast iron structures have since been transformed with design districts emerging from the ashes of these forgotten structures, infusing new life into their once-decaying shells. More recently, in the heart of London, the vibrant community of Shoreditch has flourished within the remnants of its industrial past. Former factories have been imaginatively transformed into studios, galleries and creative workspaces, attracting a new generation of artists, designers and entrepreneurs.
Similarly, the Meatpacking District in New York City underwent a remarkable metamorphosis from a gritty industrial zone to a thriving hub of fashion, art, and design. Repurposing the neighborhood’s historic meatpacking warehouses, the district now teems with high-end boutiques, galleries and avant-garde restaurants, redefining the concept of urban cool.
In the modern era, design districts have become invaluable commodities to thriving cities and the creatives who inhabit them. They serve as vibrant cultural epicenters, nurturing collaboration and cross-pollination of ideas across disciplines. These districts attract designers, artists and entrepreneurs, fueling economic growth through increased tourism, job creation and consumer spending. Their impact transcends economic gains; design districts contribute to the cultural fabric of a city, hosting exhibitions, events and festivals that celebrate creativity and artistic expression.

Shoreditch Chimney By Dani
However, patience is not a characteristic often coveted in urban development in the modern age, and today design districts may not be gifted the same lengthy development time as their predecessors. Rather than coming into existence as a natural ecosystem of designers, artists and makers drawn to an area with cheap rent and little in the way of planning restrictions, design districts are now often shaped by the vision of architects who are tasked to create places that accommodate the needs of the creative community while appealing to the broader public. Architects embarking on the design of a design district face multifaceted challenges to create authentic experiences.
The synergy of function and aesthetics lies at the core of successful design district architecture. Striking a balance between iconic structures that inspire and functional spaces that accommodate diverse businesses and creative enterprises is paramount. Architects must navigate the delicate balance between creating visually striking environments and ensuring that these districts cater to the needs and aspirations of the creative community and local residents.
Flexibility and adaptability are key considerations when designing design districts. The ability to evolve with changing trends, technologies and creative practices is crucial for their long-term success. Modular and versatile design principles that allow for easy reconfiguration are essential for fostering an environment of continuous innovation and adaptation.

Greenwich Peninsula Low Carbon Energy Centre by C.F. Møller Architects, London, England, United Kingdom. Photo by Mark Hadden
Similarly, connectivity and accessibility play pivotal roles in the design of these districts. Careful planning of transportation networks, pedestrian-friendly spaces and digital infrastructure is required to ensure the communities are accessible and inclusive. By integrating design districts with the larger urban fabric, architects foster connections, diversity and interactions, nurturing a sense of community and place.
While purposeful planning and intentional programming are important aspects of design district creation, striking a delicate balance is paramount. Single programming can inadvertently inhibit the natural “ecosystem” of different proprietors, stifling the organic growth and diversity that defines traditional neighborhoods. Design districts should feel as though they have evolved naturally, allowing for the emergence of a rich ecosystem of creative ventures and businesses intermingled with places to eat, linger and take part in cultural events. Their restaurants and music venues often define design districts.
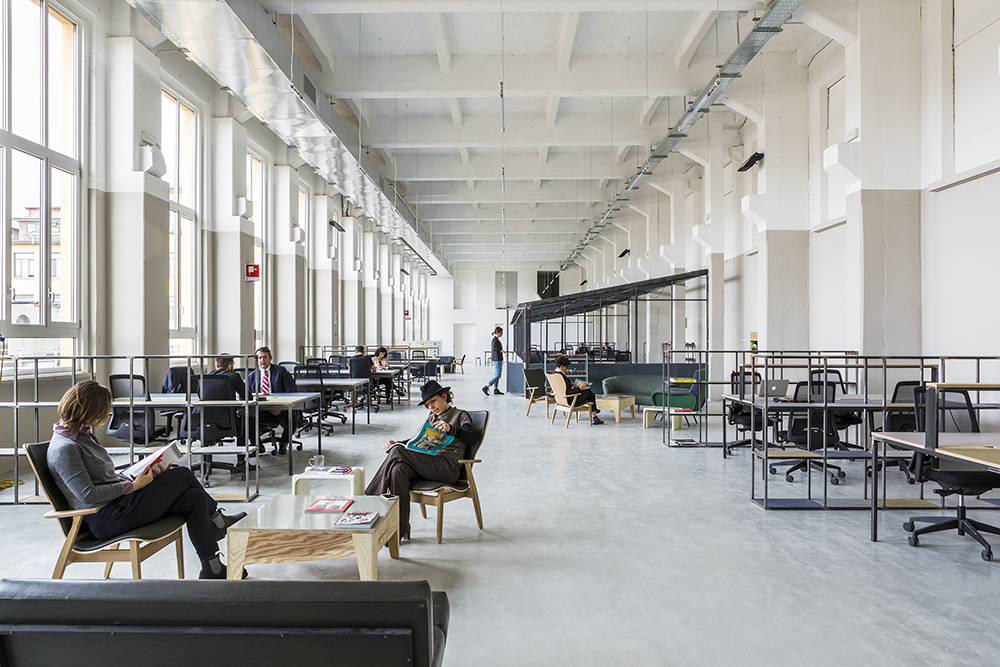

Burò Furniture by Mezzo Atelier, Milan, Italy
Purposely designing a design district is challenging, and caution should be taken against over-planning and segmenting a district into areas for function which can lead to districts failing to be vibrant homogenous neighborhoods and echoing shopping malls with an area to eat, a zone to shop, and a place to work. The Greenwich Peninsula in London has been criticized for this very reason. The purpose-built design district lacks the balance of function needed to meet the aspirations of the creative community and local residents, which is crucial for creating spaces that resonate with authenticity and a sense of belonging.
Successful design districts bear the imprints of visionary architects who have shaped these urban landscapes. Zona Tortona, Milan, Italy, was designed by a collective effort of visionary architects, including Fabio Novembre, Giulio Cappellini, and Piero Lissoni. Zona Tortona has become one of the most iconic design districts in the world and is renowned for its cutting-edge design, fashion and art events. The former industrial area now comprises sleek showrooms, galleries and creative venues. Zona Tortona’s success lies in its seamless integration of contemporary architecture and historic industrial structures, creating a captivating and vibrant atmosphere for visitors and design enthusiasts.
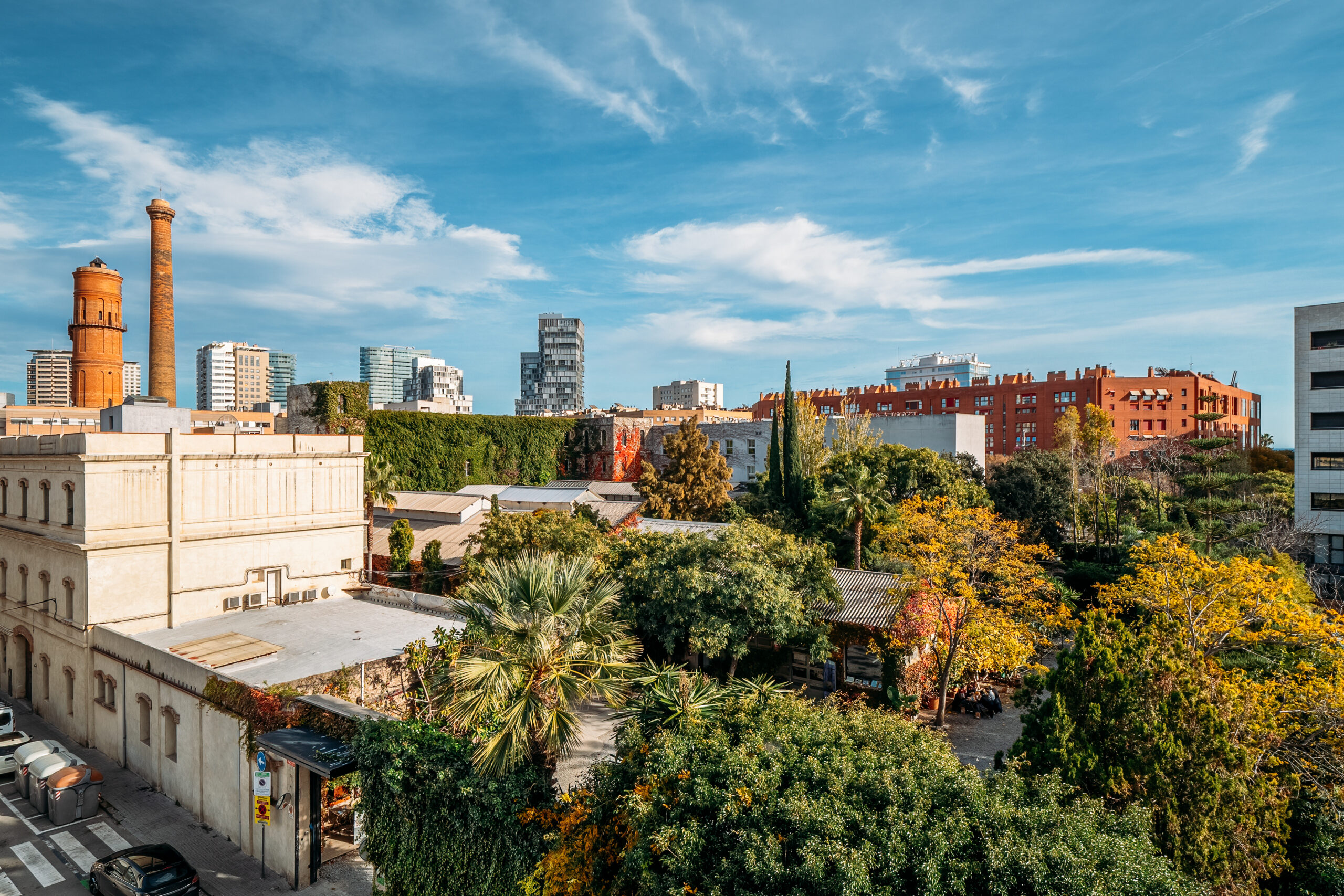

Poblenou, Barcelona, Spain by Pavel
In Barcelona, the Poblenou Design District started around twenty years ago, when artist collectives took over abandoned factories to work and host parties. Early adopters of Poblenou included the artist Antoni Miralda and Mariscal, creator of the legendary Palo Alto design studio. Although large swathes of the area still retain a gritty nature, the neighborhood is now dotted with warehouse conversions containing open-plan homes, galleries, coworking spaces and architects’ studios, making it the historic city’s creative heart.
The economic and cultural benefits of design districts are far-reaching. They attract diverse businesses, from galleries, studios and showrooms to boutiques, cafes and restaurants. The influx of visitors and tourists fuels economic growth, job creation, and increased consumer spending. Design districts become vibrant cultural epicenters, hosting exhibitions, workshops, and events that celebrate artistic expression, foster cultural exchange, and enhance the local community’s quality of life. And so, if you ever find yourself at the forefront of designing a design district, consider the marketplaces of ancient Athens, the revival of SoHo by the struggling artists of New York or the design geniuses of Barcelona and perhaps 500 years from now, your efforts will stand as a testament of great design as the streets of Grand Bazaar of Istanbul continue to do so to this day.
The judging process for Architizer's 12th Annual A+Awards is now away. Subscribe to our Awards Newsletter to receive updates about Public Voting, and stay tuned for winners announcements later this spring.
Top image: Ancient Agora of Athens in Greece by nejdetduzen