The latest edition of “Architizer: The World’s Best Architecture” — a stunning, hardbound book celebrating the most inspiring contemporary architecture from around the globe — is now available. Order your copy today.
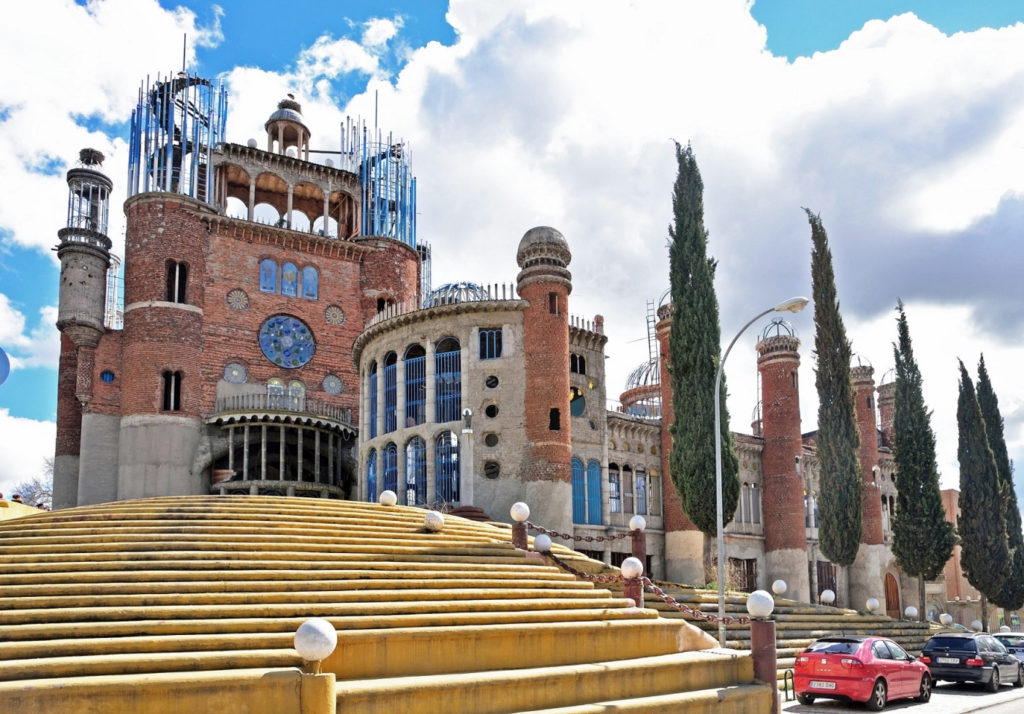
Towering over a nondescript suburb approximately 20 kilometers East of Madrid, the Cathedral of Justo Gallego provides a testament to faith in the town of Mejorada Del Campo. As the sprawling entrance steps guide you up to the entrance from the aptly named Calle de Antonio Gaudi, it is immediately clear that you are about to enter a unique architectural project. The building, nicknamed the “Cathedral of Faith”, dominates the surrounding landscape, with a 125-foot tall cupola that is visible throughout the region.
The Cathedral of Justo Gallego is a vision of recycled materials that straddles the line between a medieval ruin, salvage yard and architectural masterpiece. Its creator and sole occupant, Justo Gallego, recently passed away at the age of 96, leaving behind an ongoing project that has animated the local community, turned the area into a tourist attraction and garnered International attention over the course of the last half-century.

© Michael Piderit
Justo Gallego Martínez was born into an agricultural family in Mejorada del Campo on Sept. 20, 1925. At age 27, he joined a Trappist monastery in the Northern province of Soria, but was ordered to leave eight years later after he contracted tuberculosis and risked contaminating the other monks. Fellow acquaintances from this period in his life, including one monk in particular who studied with Justo, recall him as someone who “fasted and worked too hard,” adding that the other brothers “were worried about his health—above all, his mental health.”
After recovering from tuberculosis in a Madrid hospital, Justo returned to his hometown and decided to turn his family’s agricultural plot into a place of worship. Catalyzed by his desire to thank God for helping him survive his illness, Justo began to lay the first stones in 1961. He viewed his work as an act of faith to help return religious architecture to a classicist style based on the spiritual harmony and proportion. People in the village thought he was crazy: How could a man with so little education and so few means construct an entire cathedral from scratch by himself? “El loco de la catedral,” they called him, thoroughly convinced that he’d fail.

© Michael Piderit
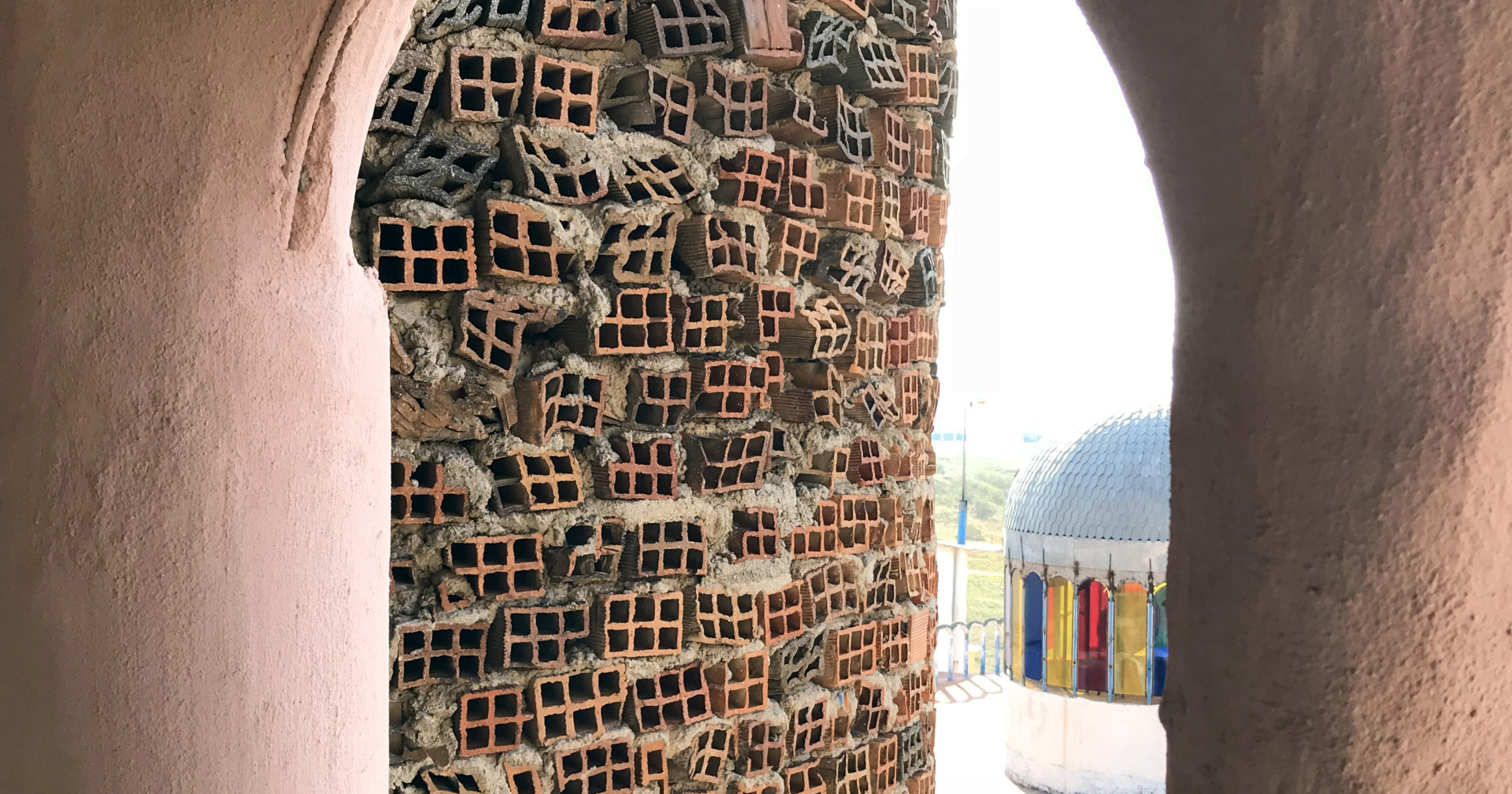
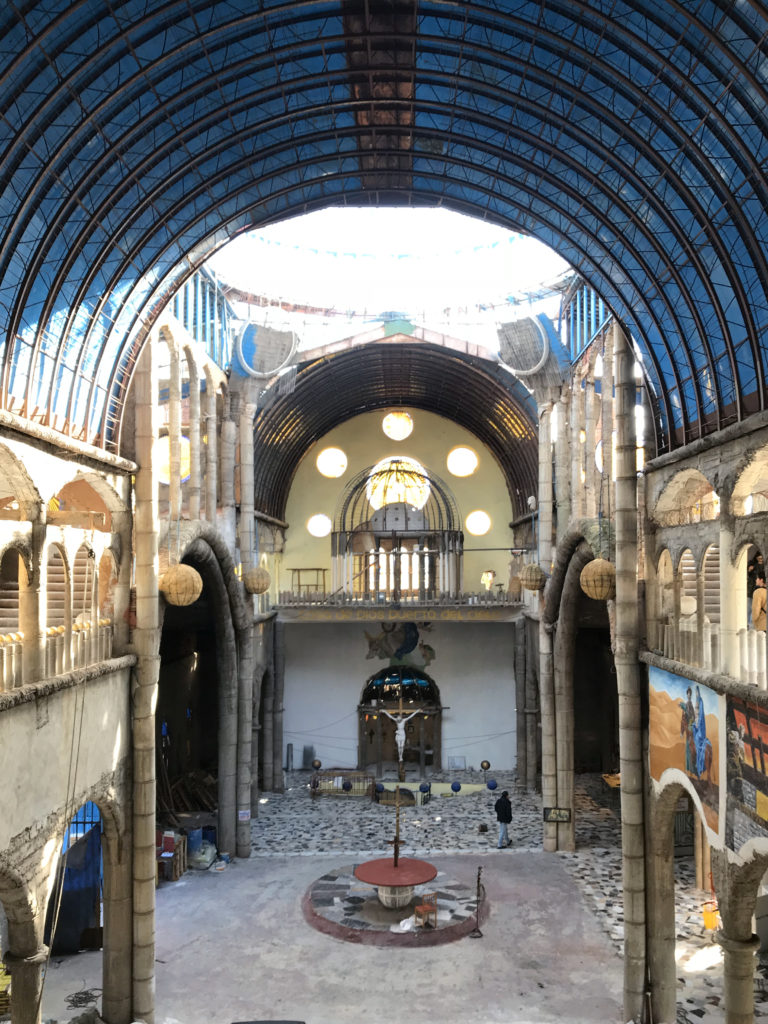
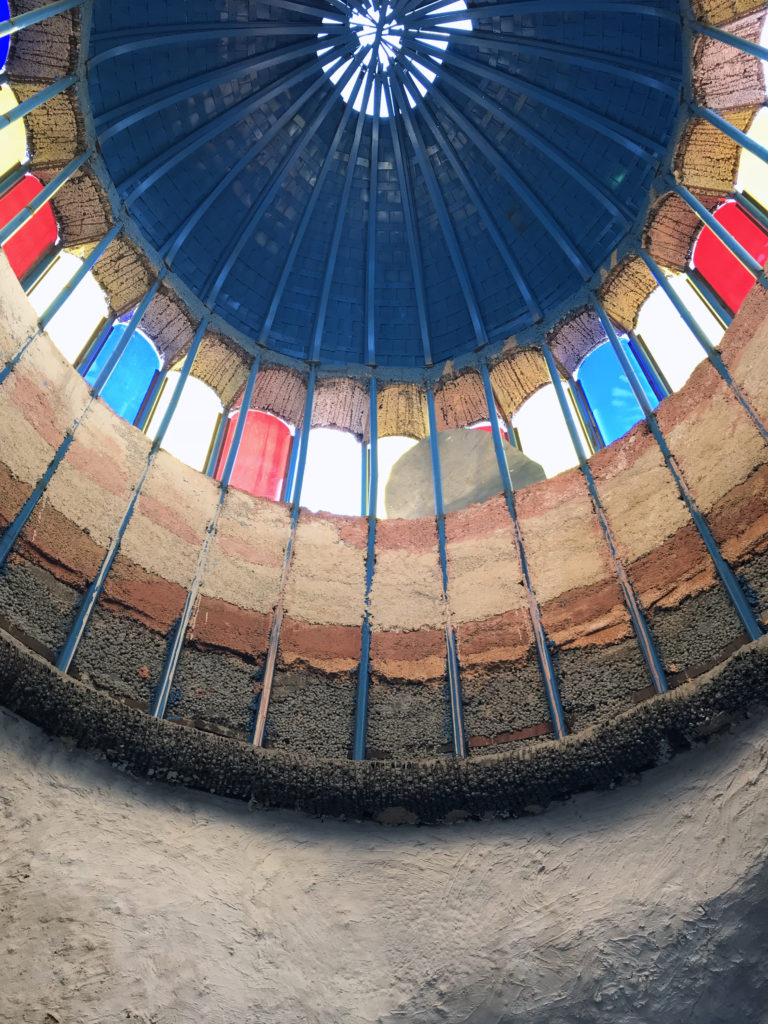
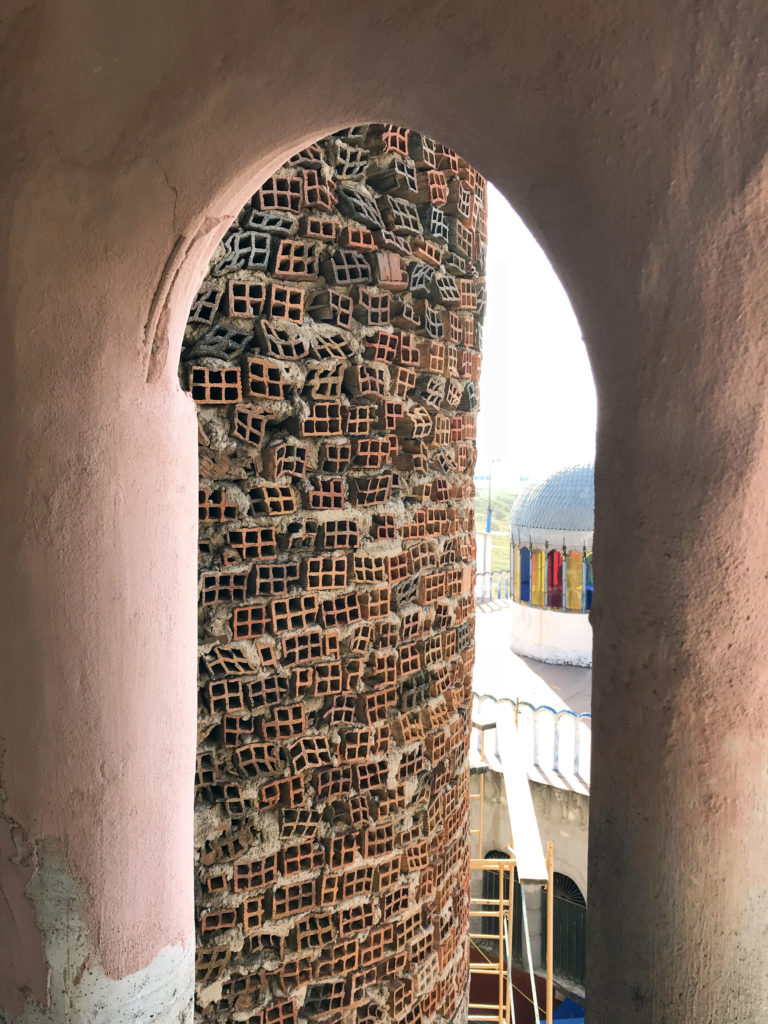
In defiance of public opinion, Justo toiled tirelessly and mostly alone to construct a cathedral complex without any architectural drawings or overall design over the course of the next 60 years. What slowly rose from the building site surprised everyone in the community. Constructed from mostly salvaged materials, the 50,590 square foot (4700 square meter) complex grew over time to contain a crypt, two cloisters, 12 towers and 28 cupolas. Decorative elements throughout the spaces utilized old tires, ceramic shards and empty metal cans. Cracked bricks and exposed metal rebar were re-interpreted as makeshift design details, giving the interior environment a precarious, raw aesthetic that creates a visual link to the materials donated over time from surrounding factories and building sites.
Justo believed in using recycled materials to build his vision, incidentally engaging in a very organic process of makeshift architectural design. As certain materials would arrive on site, his vision of each particular element of the construction would evolve. Using old car tires, bicycle wheels, unwanted materials and bricks, he effectively acted as a one man salvage yard, giving otherwise unused materials a new lease on life. In stark contrast to the architectural profession’s propensity for planning, which can constrict the spontaneous creativity of the design process, Justo’s reactive design methodology stimulated a circular economy within the region.

© Michael Piderit
Justo argued that his religious faith and determination made up for his lack of architectural training or engineering skills — his only machinery was a winch to raise stone blocks and planks — and he was unfazed by those who criticized his project as that of an eccentric monk. “The only plan is made in my head, drawn day by day,” he said. While initially widely critiqued on the grounds that the project was dangerous and being executed without proper planning permission, the local Spanish authorities ignored its existence, with neither the town council of Mejorada del Campo nor the Catholic Church wanting to take responsibility. Over time, Justo grew to become an inspirational figure within the community, recalling the history of another unfinished religious structure in Spain that has long split opinion among its residents.

© Michael Piderit
I was lucky enough to visit the Cathedral back in 2018 when Justo was still alive and at work. As we wandered through the vast spaces taking care to watch our step, I caught glimpses of Justo moving through areas of varied completion in a contemplative manner. We were aware of one another’s presence and he welcomed us to look around upon our arrival, but we treaded lightly as visitors, careful not to disturb his work.
As our tour wore on, Justo suddenly appeared and motioned us to follow him down a flight of stairs. We entered a poorly lit subterranean room, with dark plastered walls adorned with odd, spherical paper mâché ornamentation on the walls. Beyond a sea of cement bags, scattered tools and paint buckets, there was a long, deep rectangular hole cut into the earth. A modest wooden crucifix hung above it and a shovel lay on the ground. This is where Justo hoped to be laid, his self-made crypt, once he could no longer continue to build. Following his death in late 2021, town officials said they could not respect that wish after finding that the crypt did not meet Spanish sanitary rules. They buried him instead in Mejorada del Campo’s cemetery.
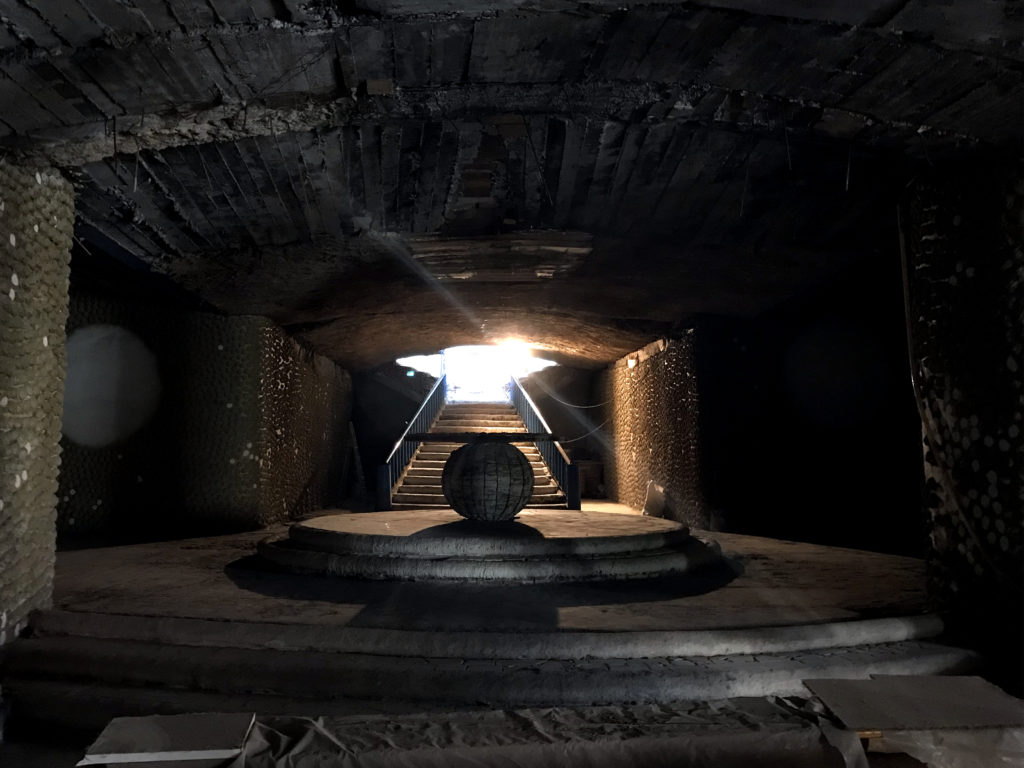

© Michael Piderit
The lack of proper documentation, including architectural drawings, safety certifications and other necessary licenses, prohibited the intended function of this building to be realized in both life and death. But to criticize the project on this front may be missing the point altogether. While Justo’s creation may never operate as an active place of communal worship, one cannot help but marvel at the singular drive of one man, whose faith emphasizes the notion that we are all works in progress, constantly striving to improve ourselves and the spaces we wish to be in.
One person in particular was taken with Justo’s mission. Upon his death, the cathedral was donated to Father Ángel, president of Mensajeros de la Paz, who intends to finish the project in order to pay homage to Justo’s life. In a recent turn of fate, a structural engineering firm that Father Angel hired deemed the building safe and structurally sound, bolstering its chances of completion. The City Council of Mejorada is also processing the application for the building to be declared a BIC (Well of Cultural Interest) by the Community of Madrid with the aim of protecting the cathedral long into the future.
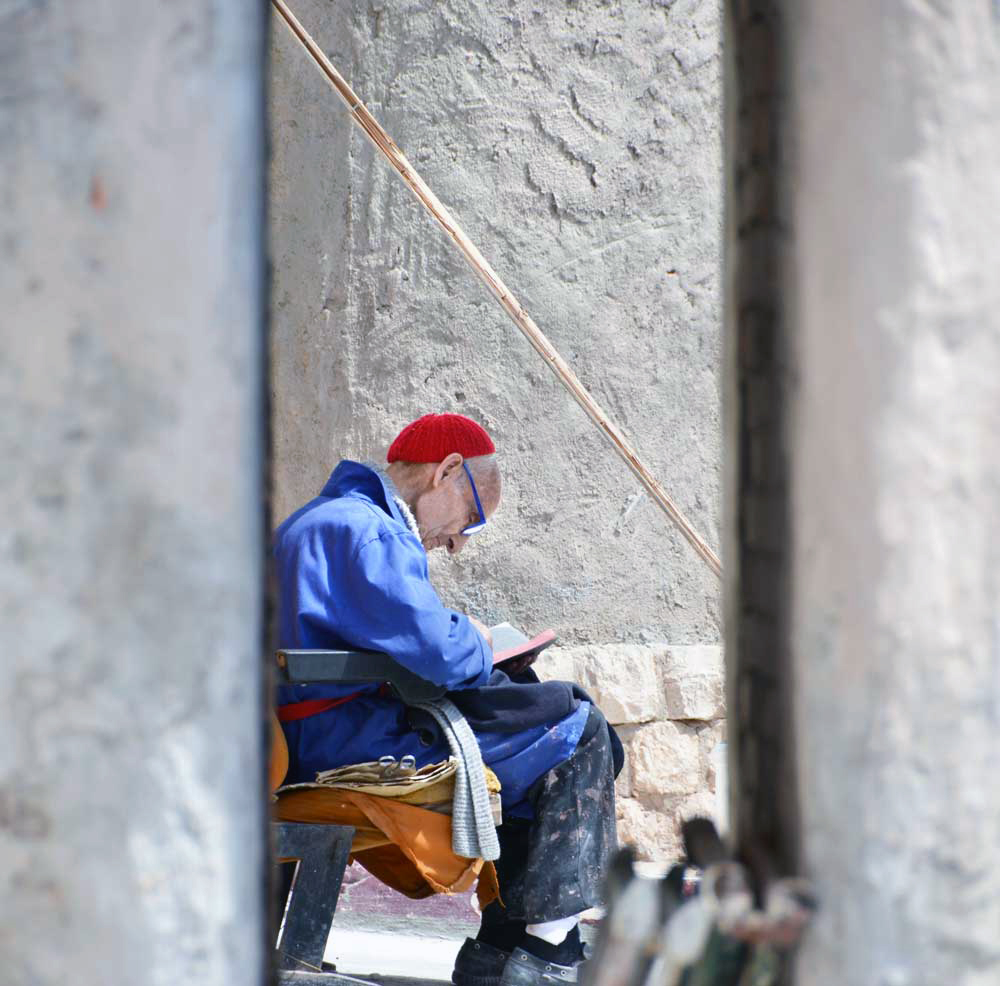

© Michael Piderit
While the fate of this cathedral still somewhat hangs in the balance, we can all learn something from Justo. The Cathedral of Justo Gallego raises important questions surrounding what it means to complete a project, and reinforces the importance of the journey over the destination. It took a single man’s singular, determined focus to block out the noise of the architecture and religious communities in pursuit of his truth. Whether or not it eventually becomes a recognized place of worship, Justo’s perseverance serves as a lesson to us all – that we are all works in progress, striving to do the best with what we have.
The latest edition of “Architizer: The World’s Best Architecture” — a stunning, hardbound book celebrating the most inspiring contemporary architecture from around the globe — is now available. Order your copy today.