Architizer's diverse jury of global experts is currently reviewing submissions to the 14th A+Awards! Sign up to receive updates on Public Voting and spring winner announcements.
Terracotta is a material that spans millennia. Durable as it is beautiful, terracotta has a range of inherent building properties that makes it an ideal choice for construction. In contemporary architecture and design, terracotta is specified as a way to redefine building envelopes with both rain screens and cladding. With a range of colors, textures, and forms, this ceramic is a material used throughout history.
Dating back to the Babylonians, terracotta continues to be a material selected for diverse building types around the world. It’s also redefining the future of how we design. By definition, architectural terracotta refers to a fired mixture of clay and water that can be used in non-structural and structural capacities on the exterior or interior of a building. Each of the following projects reinterprets terracotta and its application in diverse building types.
Pope John Paul II Hall
By Randić and Associates, Rijeka, Croati
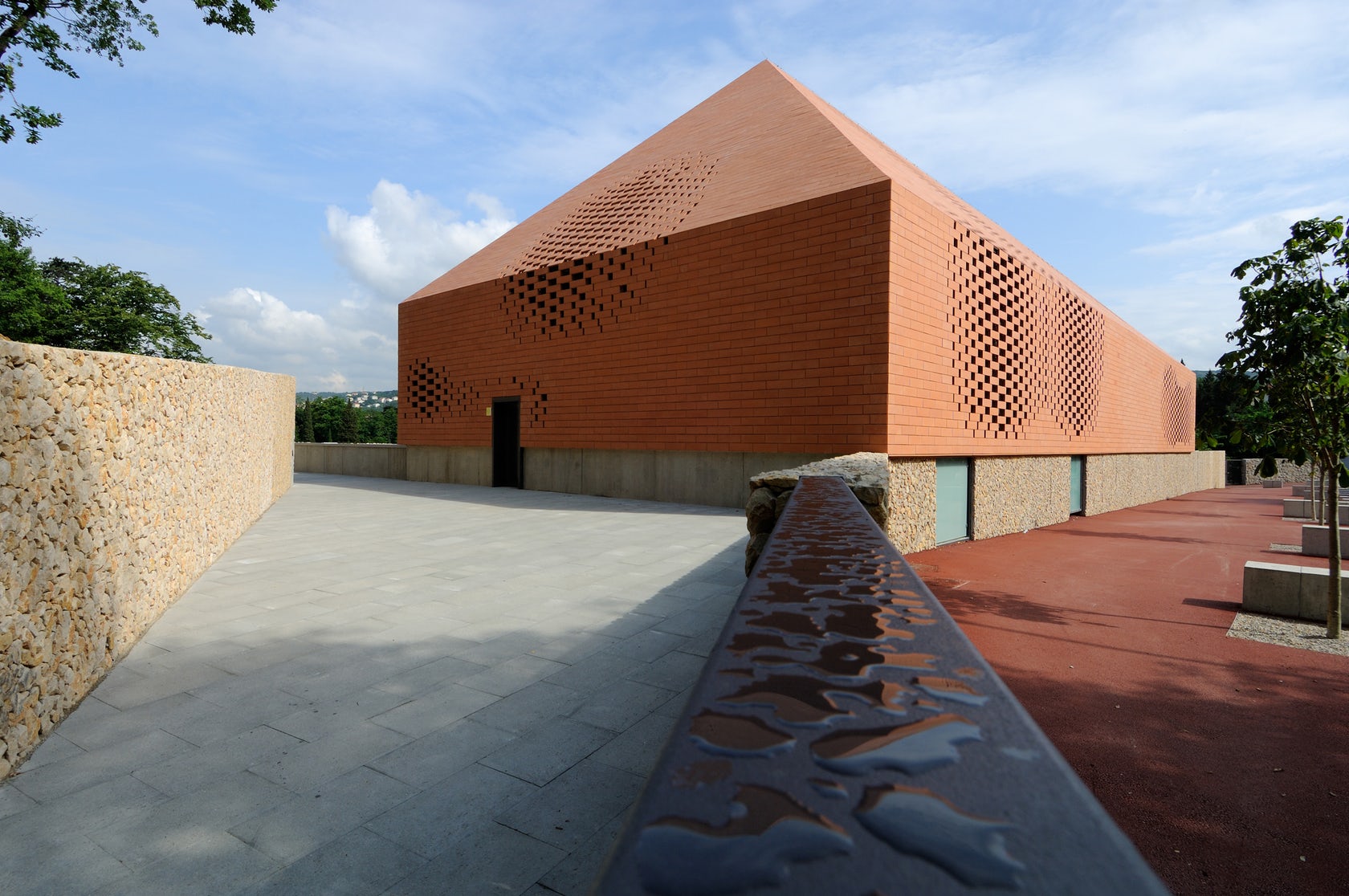
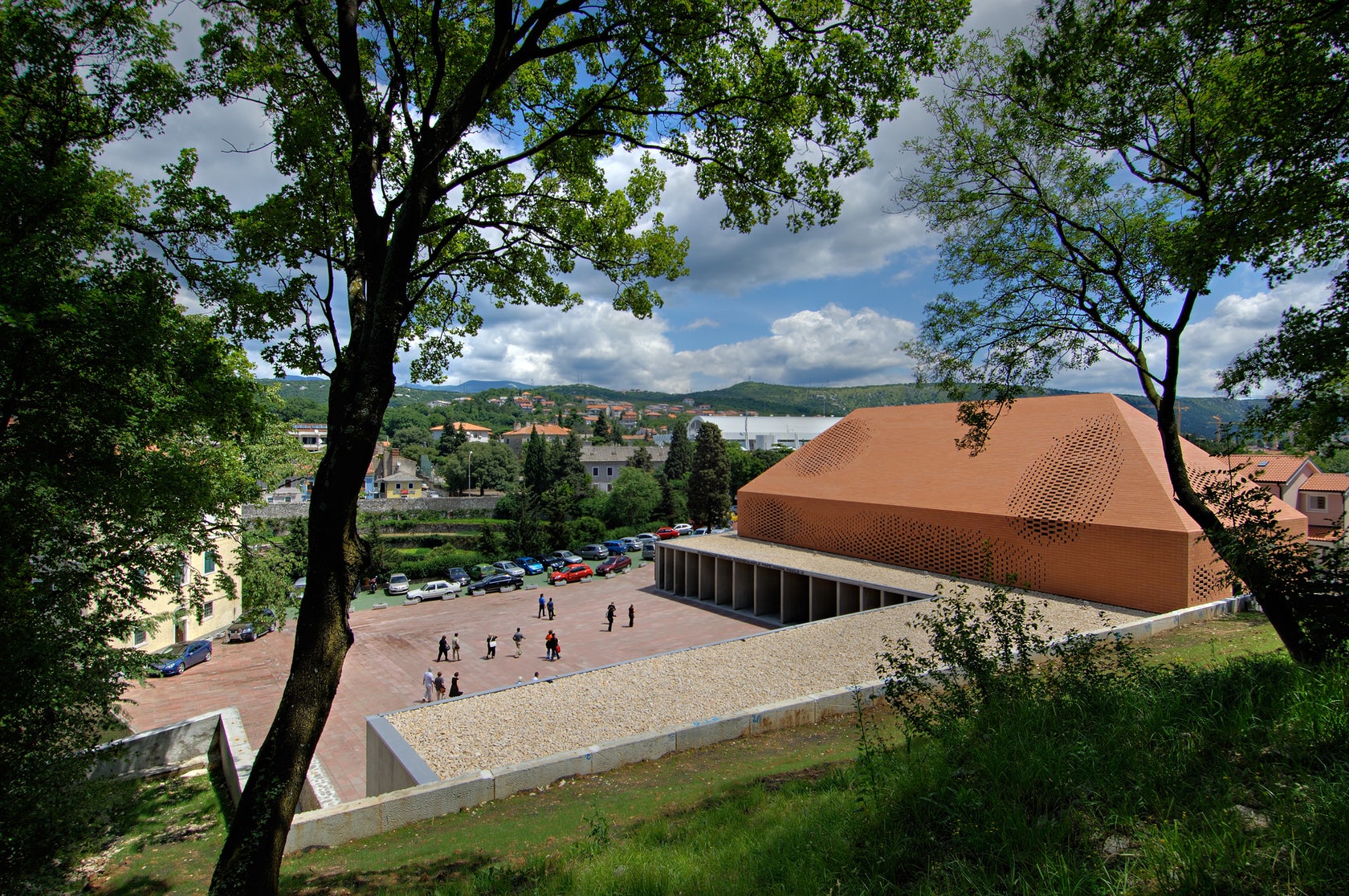
 Sited in one of the most important pilgrimage sites in Croatia, this Great Hall was designed alongside the Pope’s visit to Rijeka. Housing cultural activities of the monastery, the project also creates a new major entrance for the pilgrims and a large public walk. A pixel-ized terracotta volume was designed to filter light inside the structure while a columned portico forms a new public square outside.
Sited in one of the most important pilgrimage sites in Croatia, this Great Hall was designed alongside the Pope’s visit to Rijeka. Housing cultural activities of the monastery, the project also creates a new major entrance for the pilgrims and a large public walk. A pixel-ized terracotta volume was designed to filter light inside the structure while a columned portico forms a new public square outside.
The building features a single terracotta-brick surface. By varying the gaps between the terracotta bricks, the pixelated structure brings light into the hall. Architectural terracotta is slightly different from normal bricks, they are plain or ornamental with a glazed coating and larger in size than brick. The color goes compliments existing construction at the monastery and imitates a simple hip-roofed barn.
The Wellin Museum of Art
By Machado Silvetti, Clinton, NY, United States
TerraClad façade by Boston Valley Terra Cotta
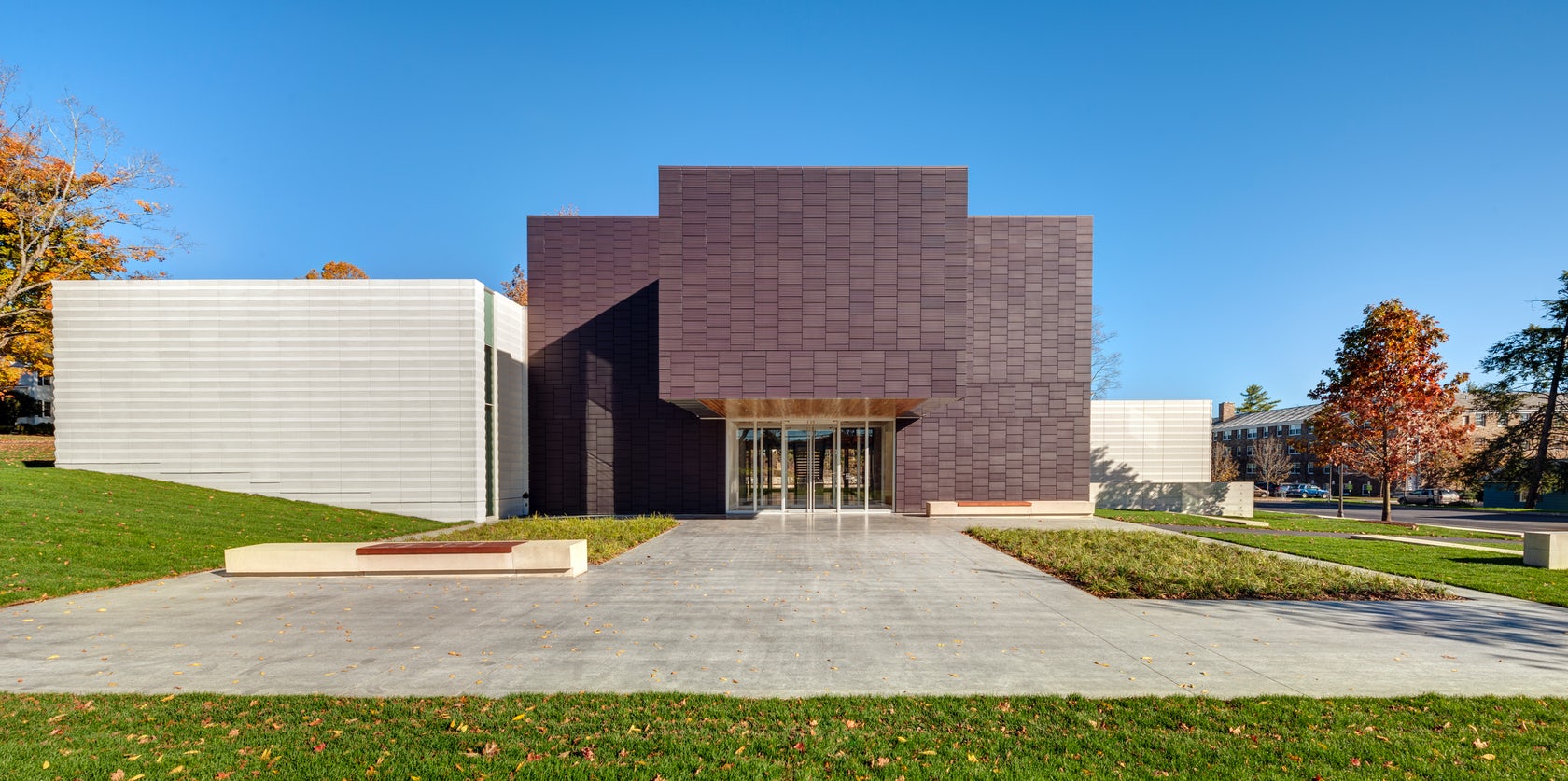
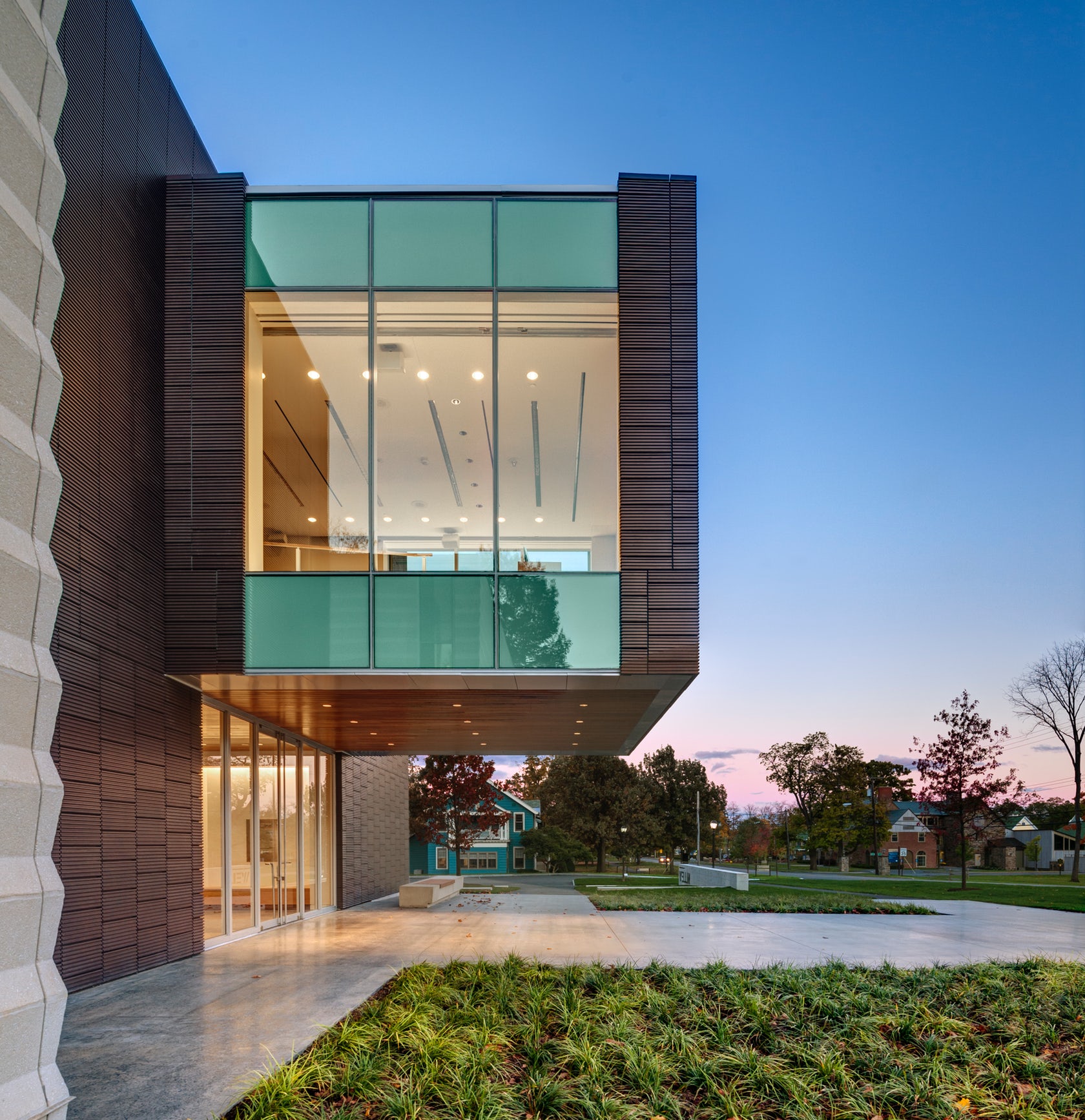
 Located on the Hamilton College campus, the Wellin Museum of art was designed as part of a new arts quad. The building includes admin offices, seminar rooms, galleries, and a monumental two-story glass archive hall. Dark terracotta cladding was used along the central volume to reinforce its role programmatically and organizationally.
Located on the Hamilton College campus, the Wellin Museum of art was designed as part of a new arts quad. The building includes admin offices, seminar rooms, galleries, and a monumental two-story glass archive hall. Dark terracotta cladding was used along the central volume to reinforce its role programmatically and organizationally.
The TerraClad façade product made by Boston Valley was forming using an extrusion method. The enclosure combines both terracotta and precast cladding with curtain wall fenestration. The system was chosen to ensure that the thermal performance of the exterior enclosure would contribute to the building’s success and meet the College’s sustainability goals.
The Diana Center at Barnard College
By WEISS / MANFREDI, New York, NY, United States
Terracotta Frit Panel by Goldray Industries
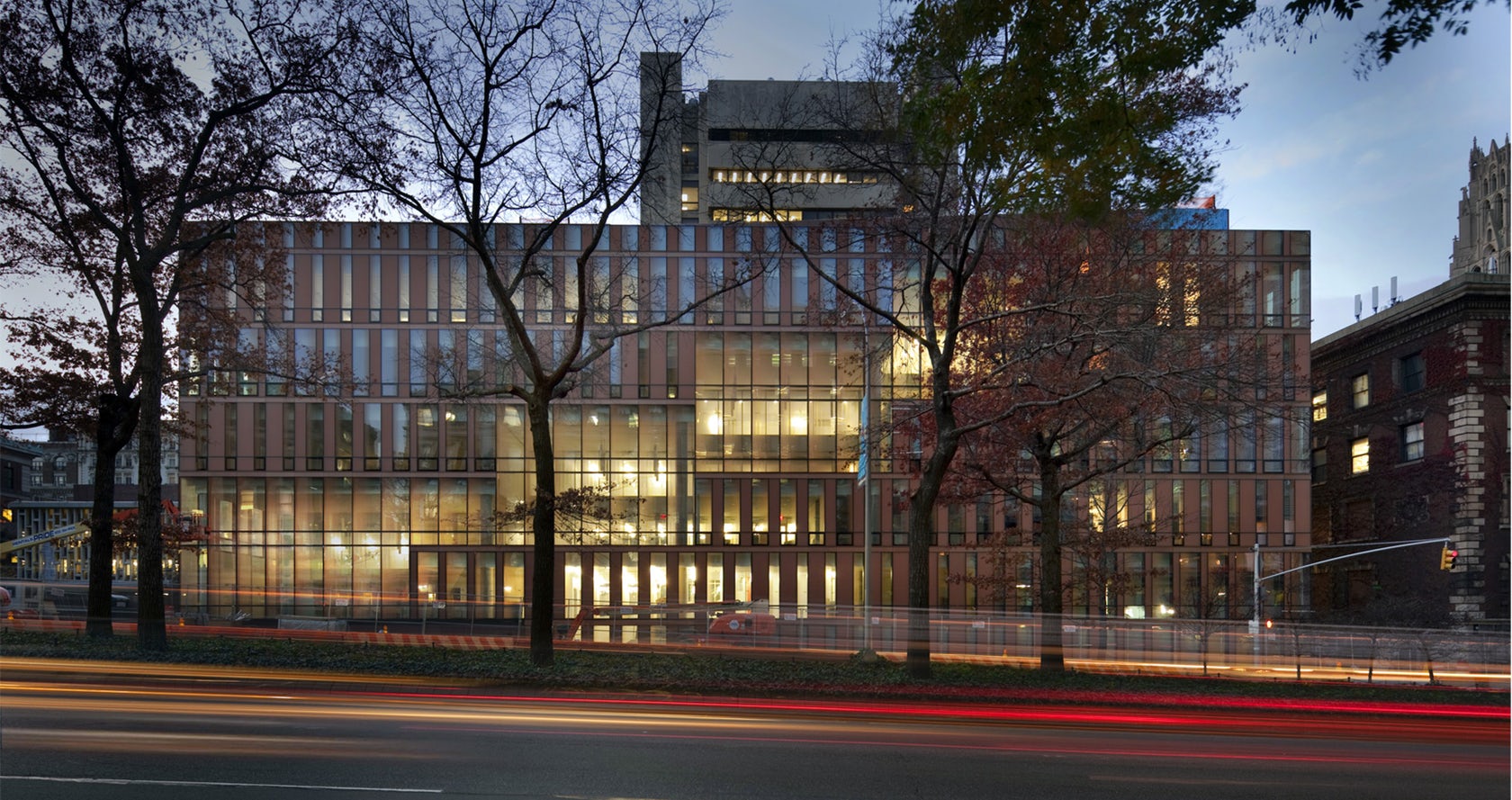
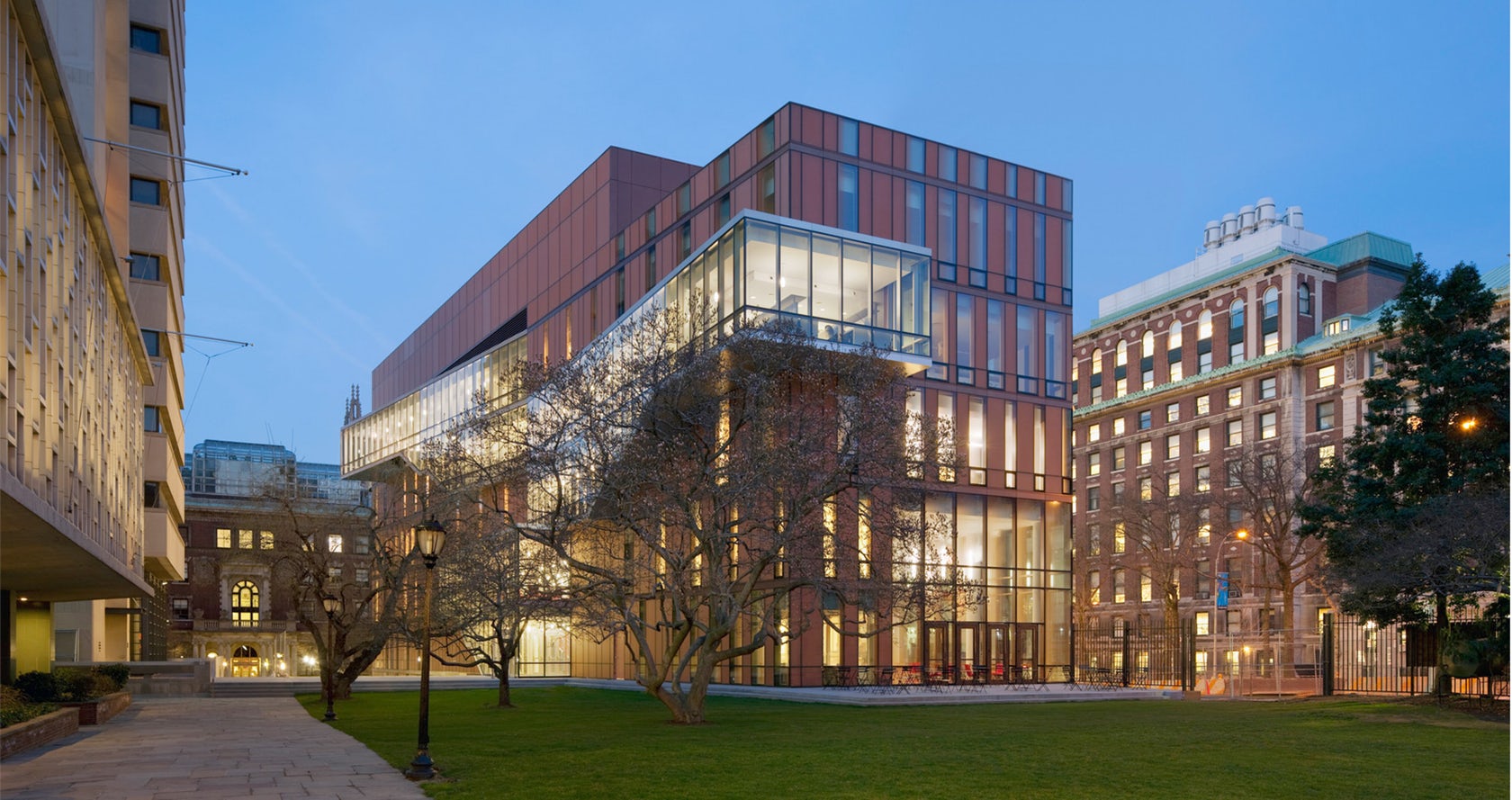
 Located at Barnard College, the Diana Center includes a gallery space, a library, classrooms, dining, and a black box theater. A slipped atria links spaces vertically and becomes connected through ascending stairs. Luminous terracotta glass panels were used throughout the building envelope. Surrounded by a campus defined by brick and terracotta, the Diana translates the static opacity of masonry into a luminous curtain wall.
Located at Barnard College, the Diana Center includes a gallery space, a library, classrooms, dining, and a black box theater. A slipped atria links spaces vertically and becomes connected through ascending stairs. Luminous terracotta glass panels were used throughout the building envelope. Surrounded by a campus defined by brick and terracotta, the Diana translates the static opacity of masonry into a luminous curtain wall.
The building’s color is created by a pale terracotta-colored frit on the #2 surface and the bright red painted back panel beneath. The glass panel, provided by Goldray Industries, is acid-etched on its exterior surface to give a matte texture, and the terracotta frit is on the interior surface.
Mercy Corps Global Headquarters
By Hacker, Portland, OR, United States
LONGOTON Terracotta Rainscreen Panels by Shildan
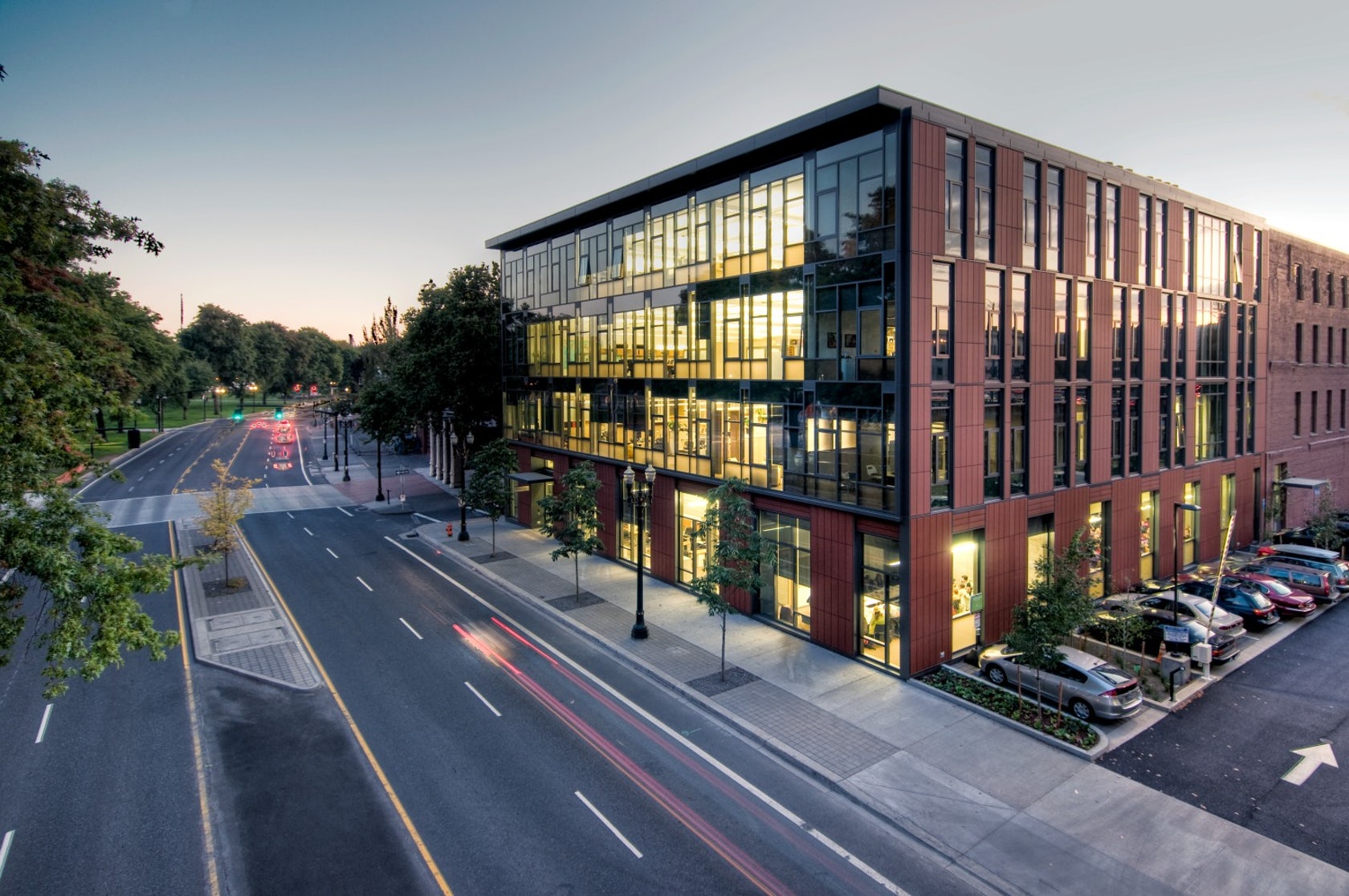
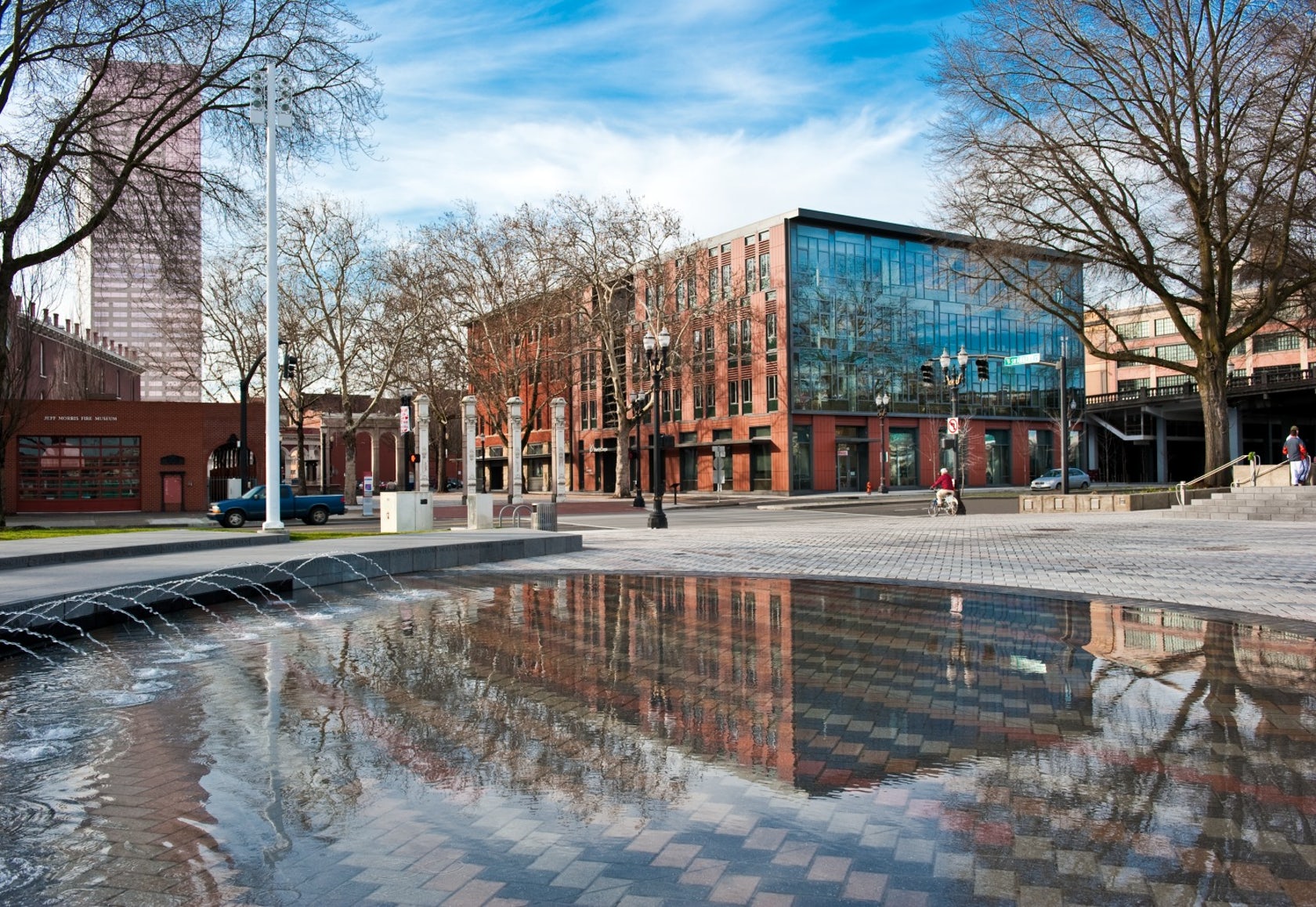
 The Mercy Corps building was built to exemplify a sustainable, community-focused approach while encouraging visitors to engage with contemporary issues. Doubling the size of the historic Portland Packer-Scott Building, the landmark project combined a green roof, with resource-friendly landscaping and a glass and terracotta envelope.
The Mercy Corps building was built to exemplify a sustainable, community-focused approach while encouraging visitors to engage with contemporary issues. Doubling the size of the historic Portland Packer-Scott Building, the landmark project combined a green roof, with resource-friendly landscaping and a glass and terracotta envelope.
Certified LEED Platinum, the project uses Shildan/Moeding LONGOTON® terracotta with extruded, double leaf, 40mm panels. The panel has increased strength from a chain of internal I-beam supports. The panels were chosen because of their flexibility in being able to be incorporated in both horizontal and vertical support systems, as well as a flexible orientation in layout.
School of Art & Design at New York State College of Ceramics
By Ikon.5 Architects, Alfred, NY, United States
Terracotta panels by Boston Valley Terra Cotta
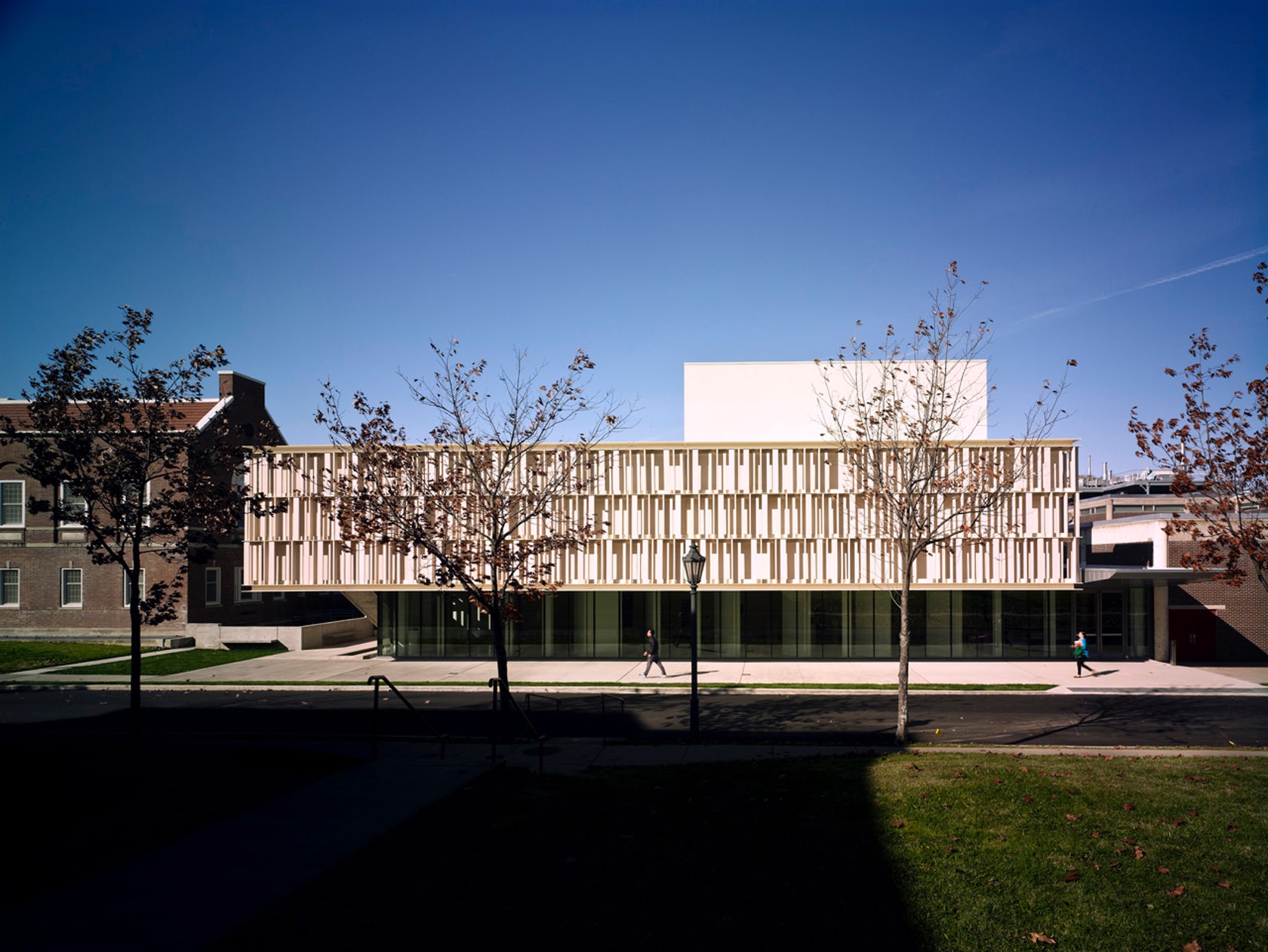
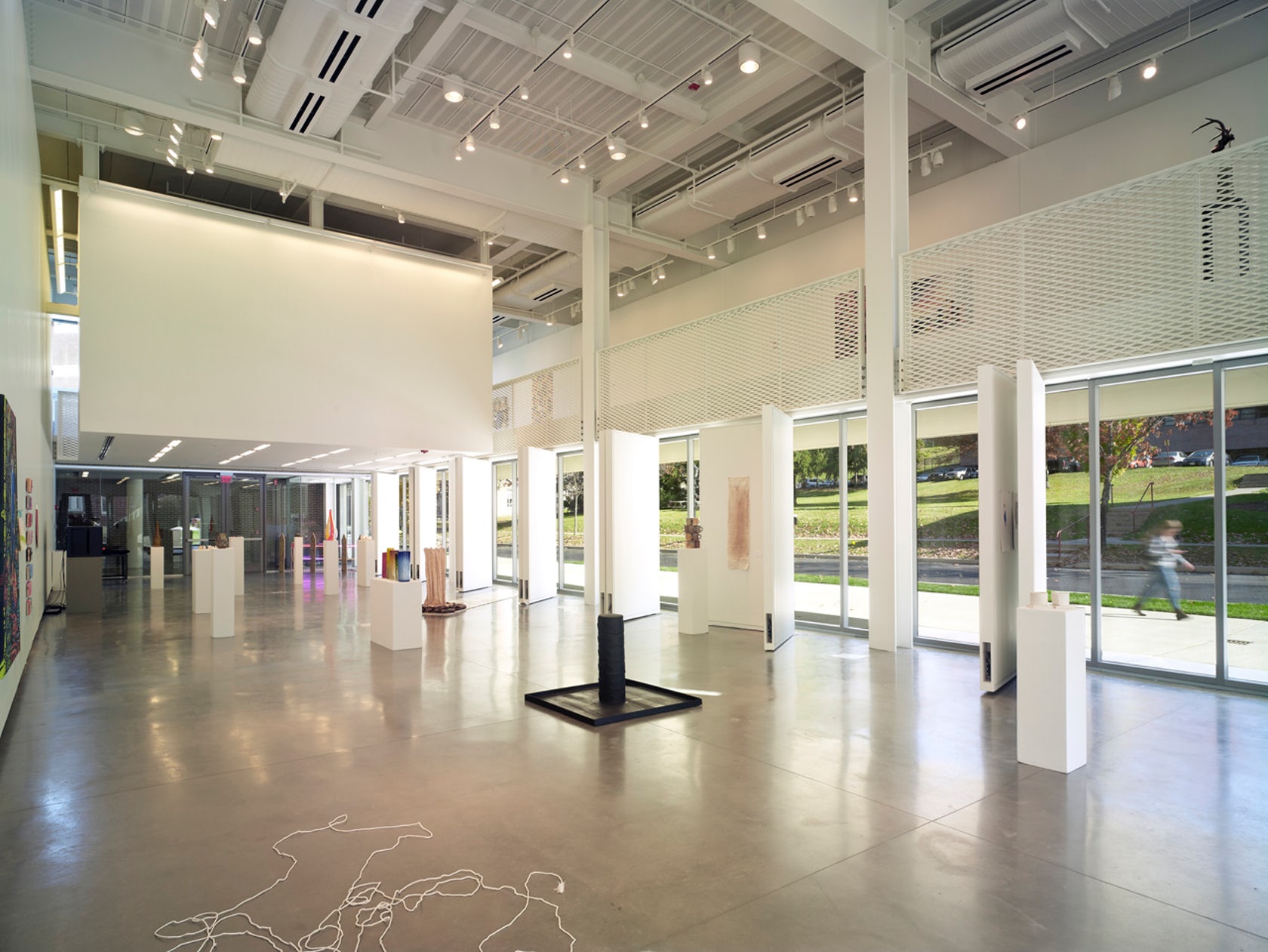
 The terracotta tube façade for this ceramics pavilion screens both rain and solar heat, while its staggered pattern was inspired by pottery racks. The Art Pavilion was created as a “ceramic vessel” holding both light and art. The design was inspired by the region’s history of manufacturing ceramics, and incorporates the unglazed, hollow tubes with an off-white pigment.
The terracotta tube façade for this ceramics pavilion screens both rain and solar heat, while its staggered pattern was inspired by pottery racks. The Art Pavilion was created as a “ceramic vessel” holding both light and art. The design was inspired by the region’s history of manufacturing ceramics, and incorporates the unglazed, hollow tubes with an off-white pigment.
Boston Valley’s terracotta façade system recalls the interior program while defining a material and haptic boundary. South-facing galleries are protected from direct sunlight, while the pavilion dramatically engages campus on-lookers as a piece of ceramic art. It allows passerby to see inside the exhibition gallery and places student work on public display.
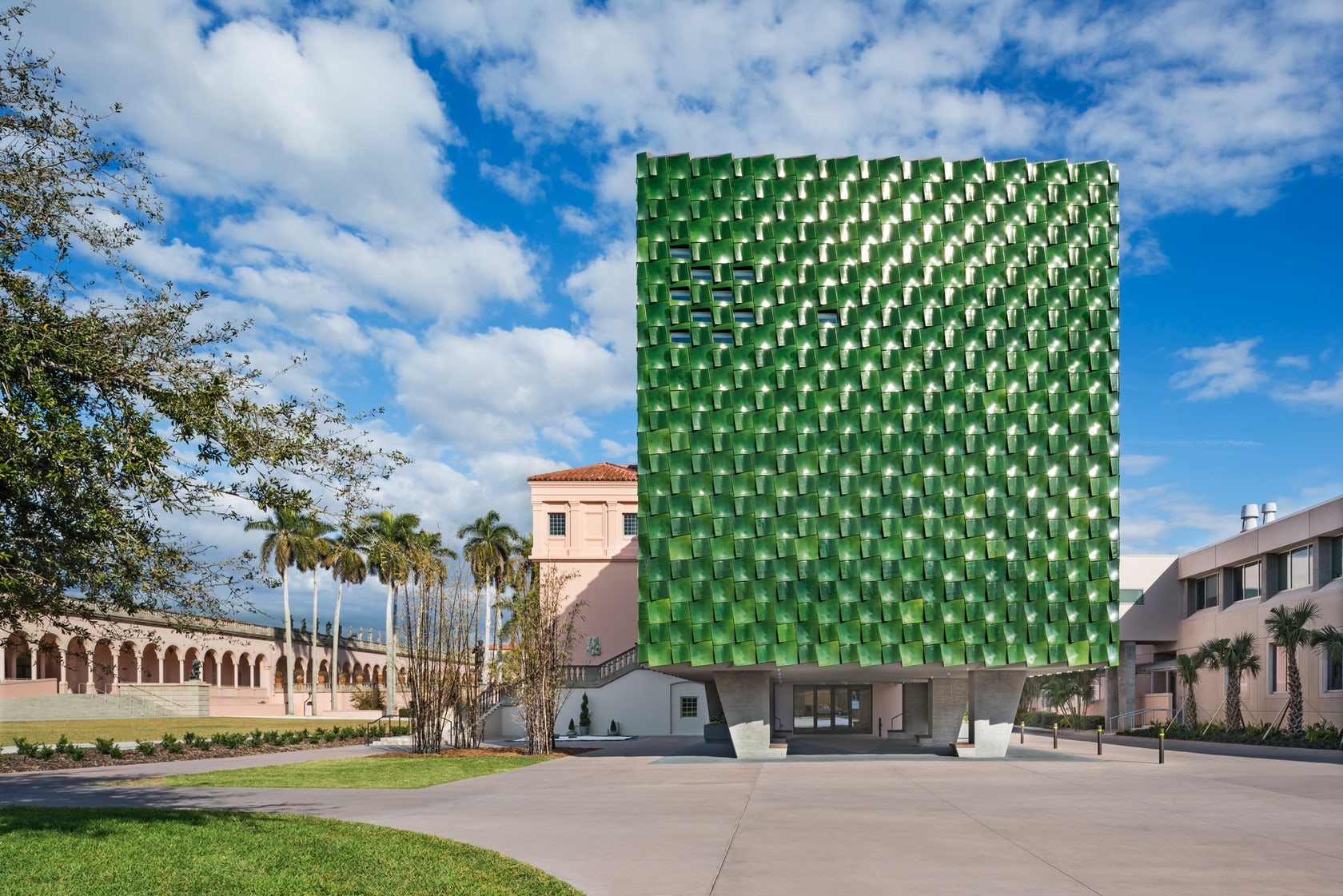
The Center for Asian Art at the Ringling Museum of Art
By Machado Silvetti, Sarasota, FL, United States
Terracotta panels by Boston Valley Terra Cotta


The John and Mable Ringling Museum of Art features both a permanent collection and temporary exhibition galleries on a historic sixty-six acre estate. Believed to be originally envisioned as one of the most comprehensive art museums in the world, the Museum was ahead of its time in assembling a significant collection of Asian Art. Now governed by Florida State University, the Museum establishes the Ringling Estate as one of the largest museum-university complexes in the United States.
The Asian Art Study Center is an addition and ‘gut renovation’ and to the West Wing galleries on the southwest corner of the Museum complex. The addition’s façade is composed of deep-green, glazed terra cotta tiles that address the client’s requirement of a new monumental entrance. Machado Silvetti collaborated closely with Boston Valley Terra Cotta to develop the color, form and installation technique for the panels.
Architizer's diverse jury of global experts is currently reviewing submissions to the 14th A+Awards! Sign up to receive updates on Public Voting and spring winner announcements.

 Mercy Corps Global Headquarters
Mercy Corps Global Headquarters  Pope John Paul II Hall
Pope John Paul II Hall  School of Art & Design at New York State College of Ceramics
School of Art & Design at New York State College of Ceramics  The Center for Asian Art at the Ringling Museum of Art
The Center for Asian Art at the Ringling Museum of Art  The Diana Center at Barnard College
The Diana Center at Barnard College  The Wellin Museum of Art
The Wellin Museum of Art 


